A population-based study on the effect of temozolomide in the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme
- PMID: 22869622
- PMCID: PMC3424214
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/nos153
A population-based study on the effect of temozolomide in the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme
Abstract
The effect of temozolomide (TMZ) and radiotherapy (RT) in the treatment of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) has been well documented in randomized controlled trials. Here we present our findings on the effect of TMZ added to RT at a population level. The Cancer Registry of Norway was searched for patients with a GBM diagnosis from January 1, 2000 to December 31, 2007. Subsequently, the prescriptions registered to these patients were obtained from the Norwegian Prescription Database. The data were analyzed according to era (pre-TMZ introduction or post-TMZ introduction) and according to treatment received. Furthermore, a matching procedure was utilized to reduce the bias between the RT + TMZ and RT alone treatments so that the effect of TMZ could be better scrutinized. We identified 1157 GBM patients. The median overall survival (OS), in months, was 8.3 (95% confidence interval: 7.6-9.0) and 10.1 (95% confidence interval: 9.1-11.0) in the pre-TMZ and TMZ eras, respectively (P < .001). By treatment, we found median OS for the control, RT alone, and RT + TMZ groups to be 2.5, 9.0, and 16.2 months, respectively (P < .001). Two-year survival was 0%, 4%, and 25%, respectively. The effect of age on TMZ effect was insignificant. In the matched group analysis, TMZ provided a 7.6-month OS benefit. Our population data reproduce the beneficial effect of TMZ from randomized controlled trials with a median OS of 16.2 months and 25% 2-year survival.
Figures
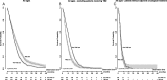
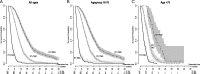
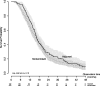
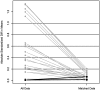
References
-
- Paszat L, Laperriere N, Groome P, Schulze K, Mackillop W, Holowaty E. A population-based study of glioblastoma multiforme. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2001;51(1):100–107. - PubMed
-
- Helseth R, Helseth E, Johannesen TB, et al. Overall survival, prognostic factors, and repeated surgery in a consecutive series of 516 patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Acta Neurol Scand. 2010;122(3):159–167. - PubMed
-
- Stummer W, Pichlmeier U, Meinel T, et al. Fluorescence-guided surgery with 5-aminolevulinic acid for resection of malignant glioma: a randomised controlled multicentre phase III trial. Lancet Oncology. 2006;7(5):392–401. - PubMed
-
- Walker MD, Green SB, Byar DP, et al. Randomized comparisons of radiotherapy and nitrosoureas for the treatment of malignant glioma after surgery. New Engl J Med. 1980;303(23):1323–1329. - PubMed
-
- Kristiansen K, Hagen S, Kollevold T, et al. Combined modality therapy of operated astrocytomas grade III and IV. Confirmation of the value of postoperative irradiation and lack of potentiation of bleomycin on survival time: a prospective multicenter trial of the Scandinavian Glioblastoma Study Group. Cancer. 1981;47(4):649–652. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

