CYP2A6- and CYP2A13-catalyzed metabolism of the nicotine Δ5'(1')iminium ion
- PMID: 22869927
- PMCID: PMC3477218
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.112.195255
CYP2A6- and CYP2A13-catalyzed metabolism of the nicotine Δ5'(1')iminium ion
Abstract
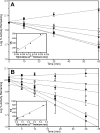
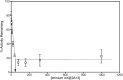
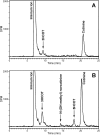
Nicotine, the major addictive agent in tobacco, is metabolized primarily by CYP2A6-catalyzed oxidation. The product of this reaction, 5'-hydroxynicotine, is in equilibrium with the nicotine Δ5'(1')iminium ion and is further metabolized to cotinine. We reported previously that both CYP2A6 and the closely related extrahepatic enzyme CYP2A13 were inactivated during nicotine metabolism; however, inactivation occurred after metabolism was complete. This led to the hypothesis that oxidation of a nicotine metabolite, possibly the nicotine Δ5'(1')iminium ion, was responsible for generating the inactivating species. In the studies presented here, we confirm that the nicotine Δ5'(1')iminium ion is an inactivator of both CYP2A6 and CYP2A13, and inactivation depends on time, concentration, and the presence of NADPH. Inactivation was not reversible and was accompanied by a parallel loss in spectrally active protein, as measured by reduced CO spectra. These data are consistent with the characterization of the nicotine Δ5'(1')iminium ion as a mechanism-based inactivator of both CYP2A13 and CYP2A6. We also confirm that both CYP2A6 and CYP2A13 catalyze the metabolism of the nicotine Δ5'(1')iminium ion to cotinine and provide evidence that both enzymes catalyze the sequential metabolism of the nicotine Δ5'(1')iminium ion. That is, a fraction of the cotinine formed may not be released from the enzyme before further oxidation to 3'-hydroxycotinine.
Figures
References
-
- Bao Z, He XY, Ding X, Prabhu S, Hong JY. (2005) Metabolism of nicotine and cotinine by human cytochrome P450 2A13. Drug Metab Dispos 33:258–261 - PubMed
-
- Brandänge S, Lindblom L. (1979) The enzyme “aldehyde oxidase” is an iminium oxidase. Reaction with nicotine Δ1′(5′) iminium ion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 91:991–996 - PubMed
-
- Brown KM, von Weymarn LB, Murphy SE. (2005) Identification of N-(hydroxymethyl) norcotinine as a major product of cytochrome P450 2A6, but not cytochrome P450 2A13-catalyzed cotinine metabolism. Chem Res Toxicol 18:1792–1798 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

