Soluble VEGF receptor-2 may be a predictive marker of anti-angiogenic therapy with clinically available safe agents
- PMID: 22870131
- PMCID: PMC3412527
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2010.196
Soluble VEGF receptor-2 may be a predictive marker of anti-angiogenic therapy with clinically available safe agents
Abstract
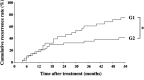
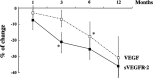
The identification of biomarkers of anti-angiogenic therapy that predict clinical benefit is of vital importance. We previously reported that a combination treatment with clinically available safe agents, specifically angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (ACE-I) and vitamin K (VK), inhibited the cumulative recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) via suppression of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). The present study aimed to identify non-invasive biological markers that predict the clinically beneficial effect of this combination regimen. A combination of ACE-I (perindopril; 4 mg/day) and VK (menatetrenone; 45 mg/day) was administered for 54 months following curative therapy for HCC. The cumulative recurrence and several indices, which are reportedly considered as biological markers of anti-angiogenic therapies, were analyzed. The combined treatment of ACE-I and VK markedly inhibited the cumulative recurrence of HCC during the 54-month follow-up. The serum VEGF and soluble VEGF receptor (sVEGFR)-2 were significantly suppressed with this combination regimen, whereas sVEGFR-1 was not. In HCC patients without recurrence, a significant suppression of VEGF and sVEGFR-2 was achieved within 6 and 3 months after treatment, respectively. In conclusion, the combination treatment of ACE-I and VK is a potentially novel anti-angiogenic strategy for secondary chemoprevention against HCC since the two agents are widely used in clinical practice without serious side effects. Furthermore, sVEGFR-2 may become a useful clinical predictive marker of this combination treatment.
Figures
References
-
- Schafer DF, Sorrell MF. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 1999;353:1253–1257. - PubMed
-
- Kerbel RS. Tumor angiogenesis: past, present and the near future. Carcinogenesis. 2000;21:505–515. - PubMed
-
- Guo RP, Zhong C, Shi M, et al. Clinical value of apoptosis and angiogenesis factors in estimating the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2006;132:547–555. - PubMed
-
- Iavarone M, Lampertico P, Iannuzzi F, et al. Increased expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in small hepatocellular carcinoma. J Viral Hepat. 2007;14:133–139. - PubMed
-
- Li CY, Shan S, Huang Q, et al. Initial stages of tumor cell-induced angiogenesis: evaluation via skin window chambers in rodent models. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92:143–147. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
