Association of HLA-DR1 with the allergic response to the major mugwort pollen allergen: molecular background
- PMID: 22871092
- PMCID: PMC3522052
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2172-13-43
Association of HLA-DR1 with the allergic response to the major mugwort pollen allergen: molecular background
Abstract
Background: Mugwort pollen allergens represent the main cause of pollinosis in late summer. The major allergen, Art v 1, contains only one single immunodominant, solely HLA-DR-restricted T cell epitope (Art v 125-36). The frequency of HLA-DRB1*01 is highly increased in mugwort-allergic individuals and HLA-DR1 serves as restriction element for Art v 125-36. However, Art v 125-36 also binds to HLA-DR4 with high affinity and DR1-restricted Art v 125-36 -specific T cell receptors can be activated by HLA-DR4 molecules. To understand the predominance of HLA-DR1 in mugwort allergy in spite of the degeneracy in HLA/peptide-binding and TCR-recognition, we investigated the molecular background of Art v 125-36 /MHC/TCR interactions in the context of HLA-DR1 compared to -DR4.
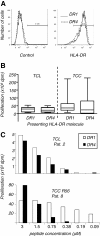
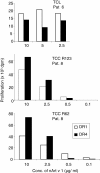
Results: The majority of Art v 125-36 -specific T cell lines and clones from HLA-DR1 carrying, mugwort pollen-allergic donors reacted to synthetic and naturally processed Art v 1-peptides when presented by HLA-DR1 or HLA-DR4 expressing antigen presenting cells. However, at limiting peptide concentrations DR1 was more effective in T cell stimulation. In addition, the minimal epitope for 50% of Art v 125-36 -specific T cells was shorter for DR1 than for DR4. In vitro binding assays of Art v 125-36 mutant peptides to isolated DR1- and DR4-molecules indicated similar binding capacities and use of the same register. In silico simulation of Art v 125-36 binding to HLA-DR1 and -DR4 suggested similar binding of the central part of the peptide to either molecule, but a higher flexibility of the N- and C-terminal amino acids and detachment at the C-terminus in HLA-DR1.
Conclusions: The predominance of HLA-DR1 in the response to Art v 125-36 may be explained by subtle conformation changes of the peptide bound to DR1 compared to DR4. Computer simulation supported our experimental data by demonstrating differences in peptide mobility within the HLA-DR complex that may influence TCR-binding. We suggest that the minor differences observed in vitro may be more relevant in the microenvironment in vivo, so that only presentation by HLA-DR1, but not -DR4 permits successful T cell activation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Characterization of HLA class II/peptide-TCR interactions of the immunodominant T cell epitope in Art v 1, the major mugwort pollen allergen.J Immunol. 2008 Sep 1;181(5):3636-42. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.5.3636. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18714038
-
Antigen presentation of the immunodominant T-cell epitope of the major mugwort pollen allergen, Art v 1, is associated with the expression of HLA-DRB1 *01.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005 Feb;115(2):399-404. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2004.10.010. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15696102
-
The T cell response to Art v 1, the major mugwort pollen allergen, is dominated by one epitope.J Immunol. 2002 Nov 15;169(10):6005-11. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.10.6005. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12421987
-
The spectrum of allergens in ragweed and mugwort pollen.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2005 Dec;138(4):337-46. doi: 10.1159/000089188. Epub 2005 Oct 24. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16254437 Review.
-
TCR recognition of peptide/MHC class II complexes and superantigens.Semin Immunol. 2007 Aug;19(4):262-71. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2007.04.006. Epub 2007 Jun 7. Semin Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17560120 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
T Cell Epitope Peptide Therapy for Allergic Diseases.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016 Feb;16(2):14. doi: 10.1007/s11882-015-0587-0. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016. PMID: 26768622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) Class I and MHC Class II Proteins: Conformational Plasticity in Antigen Presentation.Front Immunol. 2017 Mar 17;8:292. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00292. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28367149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptide-induced immune regulation by a promiscuous and immunodominant CD4T-cell epitope of Timothy grass pollen: a role of Cbl-b and Itch in regulation.Thorax. 2014 Apr;69(4):335-45. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2013-204324. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Thorax. 2014. PMID: 24258832 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoregulatory T cell epitope peptides: the new frontier in allergy therapy.Clin Exp Allergy. 2015 Jun;45(6):1015-26. doi: 10.1111/cea.12554. Clin Exp Allergy. 2015. PMID: 25900315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Large scale characterization of the LC13 TCR and HLA-B8 structural landscape in reaction to 172 altered peptide ligands: a molecular dynamics simulation study.PLoS Comput Biol. 2014 Aug 7;10(8):e1003748. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003748. eCollection 2014 Aug. PLoS Comput Biol. 2014. PMID: 25101830 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ou D, Mitchell LA, Tingle AJ. HLA-DR restrictive supertypes dominate promiscuous T cell recognition: association of multiple HLA-DR molecules with susceptibility to autoimmune diseases. J Rheumatol. 1997;24:253–261. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

