Controlled delivery of bioactive molecules into live cells using the bacterial mechanosensitive channel MscL
- PMID: 22871809
- PMCID: PMC3651673
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms1999
Controlled delivery of bioactive molecules into live cells using the bacterial mechanosensitive channel MscL
Abstract
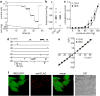
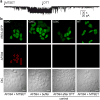
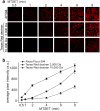
Bacterial mechanosensitive channels are some of the largest pores in nature. In particular, MscL, with a pore diameter >25 Å, allows passage of large organic ions and small proteins. Functional MscL reconstitution into lipids has been proposed for applications in vesicular-based drug release. Here we show that these channels can be functionally expressed in mammalian cells to afford rapid controlled uptake of membrane-impermeable molecules. We first demonstrate that MscL gating in response to increased membrane tension is preserved in mammalian cell membranes. Molecular delivery is controlled by adopting an established method of MscL charge-induced activation. We then determine pore size limitations using fluorescently labelled model cargoes. Finally, we activate MscL to introduce the cell-impermeable bi-cyclic peptide phalloidin, a specific marker for actin filaments, into cells. We propose that MscL will be a useful tool for gated and controlled delivery of bioactive molecules into cells.
Figures

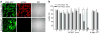
References
-
- Hamill OP, Martinac B. Molecular basis of mechanotransduction in living cells. Physiol Rev. 2001;81:685–740. - PubMed
-
- Martinac B. Mechanosensitive ion channels: molecules of mechanotransduction. J Cell Sci. 2004;117:2449–2460. - PubMed
-
- Sukharev SI, Blount P, Martinac B, Blattner FR, Kung C. A large-conductance mechanosensitive channel in E.coli encoded by mscL alone. Nature. 1994;368:265–268. - PubMed
-
- Blount P, Schroeder MJ, Kung C. Mutations in a bacterial mechanosensitive channel change the cellular response to osmotic stress. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:32150–32157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

