Prevalence of peripheral abnormalities on ultra-widefield greenlight (532 nm) autofluorescence imaging at a tertiary care center
- PMID: 22871828
- PMCID: PMC3450919
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.12-9909
Prevalence of peripheral abnormalities on ultra-widefield greenlight (532 nm) autofluorescence imaging at a tertiary care center
Abstract
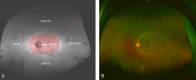
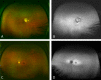
Purpose: To assess the prevalence of peripheral fundus autofluorescence (FAF) abnormalities in a variety of diseases seen at a tertiary retina clinic.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective review of cases seen at the Doheny Eye Institute between November 2009 and May 2011, who had ultra-widefield FAF and pseudocolor imaging performed on new models of scanning laser ophthalmoscopes. Patients with a history of previous therapies that could alter the FAF findings, including vitrectomy, cryotherapy, laser photocoagulation, or photodynamic therapy, were excluded from the analysis. Based on their primary diagnosis the eyes were grouped into nine disease categories: age-related macular degeneration, central serous retinopathy, dystrophy, inflammatory disorders, ocular tumor, retinal vascular disorders, other, normal, and unknown. All FAF and accompanying pseudocolor images were reviewed independently by two reading center-certified graders.
Results: A total of 470 eyes of 248 patients were included for analysis of which 461 eyes had images of sufficient quality for grading. The prevalence of peripheral findings was 65.5% (n = 302) for FAF images and 68.5% (n = 316) for the pseudocolor images (P < 0.001). The prevalence of peripheral abnormalities differed significantly between the disease categories ranging from 18.5% to 82.2% for FAF and 18.5% to 82.4% for pseudocolor images.
Conclusions: Peripheral FAF abnormalities are frequent and readily revealed by FAF imaging. Interestingly, even cases with presumably macular disease demonstrated a high prevalence of peripheral findings. Further investigation in prospective studies is warranted.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures
References
-
- Lai TYY, Fan DSP, Lai WWK, Lam DSC. Peripheral and posterior pole retinal lesions in association with high myopia: a cross-sectional community-based study in Hong Kong. Eye. 2008;22:209–213 - PubMed
-
- Coffee RE, Jain A, McCannel TA. Ultra wide-field imaging of choroidal metastasis secondary to primary breast cancer. Semin Ophthalmol. 2009;24:34–36 - PubMed
-
- Mantel I, Uffer S, Zografos L. Peripheral exudative hemorrhagic chorioretinopathy: a clinical, angiographic, and histologic study. AJOPHT. 2009;148:932–938 - PubMed
-
- Delori FC, Goger DG, Dorey CK. Age-related accumulation and spatial distribution of lipofuscin in RPE of normal subjects. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001;42:1855–1866 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

