Electrophysiological effects of repeated administration of agomelatine on the dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin systems in the rat brain
- PMID: 22871919
- PMCID: PMC3527117
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2012.140
Electrophysiological effects of repeated administration of agomelatine on the dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin systems in the rat brain
Abstract
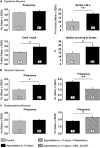
Agomelatine is a melatonergic MT1/MT2 agonist and a serotonin (5-HT) 5-HT(2C) antagonist. The effects of 2-day and 14-day administration of agomelatine were investigated on the activity of ventral tegmental area (VTA) dopamine (DA), locus coeruleus (LC) norepinephrine (NE), and dorsal raphe nucleus (DRN) 5-HT neurons using in vivo electrophysiology in rats. The 5-HT(1A) transmission was assessed at hippocampus CA3 pyramidal neurons. After a 2-day regimen of agomelatine (40 mg/kg/day, i.p.), an increase in the number of spontaneously active VTA-DA neurons (p<0.001) and in the firing rate of LC-NE neurons (p<0.001) was observed. After 14 days, the administration of agomelatine induced an increase in: (1) the number of spontaneously active DA neurons (p<0.05), (2) the bursting activity of DA neurons (bursts/min, p<0.01 and percentage of spikes occurring in bursts, p<0.05), (3) the firing rate of DRN-5-HT neurons (p<0.05), and (4) the tonic activation of postsynaptic 5-HT(1A) receptors located in the hippocampus. The increase in 5-HT firing rate was D2 dependent, as it was antagonized by the D2 receptor antagonist paliperidone. The enhancement of NE firing was restored by the 5-HT(2A) receptor antagonist MDL-100,907 after the 14-day regimen. All the effects of agomelatine were antagonized by a single administration of the melatonergic antagonist S22153 (except for the increase in the percentage of spikes occurring in burst for DA neurons). The present results suggest that (1) agomelatine exerts direct (2 days) and indirect (14 days) modulations of monoaminergic neuronal activity and (2) the melatonergic agonistic activity of agomelatine contributes to the enhancement of DA and 5-HT neurotransmission.
Figures



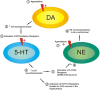
 Agomelatine (14 days) induced an excitatory effect on DA cells in the VTA (increase in the number of neuron spontaneously active and bursting activity) that resulted in
Agomelatine (14 days) induced an excitatory effect on DA cells in the VTA (increase in the number of neuron spontaneously active and bursting activity) that resulted in  an increase in DA neurotransmission, leading to
an increase in DA neurotransmission, leading to  the activation of excitatory D2 receptors located on DRN-5-HT cells.
the activation of excitatory D2 receptors located on DRN-5-HT cells.  The corresponding increase in 5-HT firing activity then induced
The corresponding increase in 5-HT firing activity then induced  an activation of the excitatory 5-HT2A receptors located on GABA interneurons. The increase in GABA activity induced
an activation of the excitatory 5-HT2A receptors located on GABA interneurons. The increase in GABA activity induced  an inhibition of LC-NE neurons. However,
an inhibition of LC-NE neurons. However,  agomelatine by itself also exerts an excitatory effect on LC-NE neurons (as seen after a 2-day treatment).
agomelatine by itself also exerts an excitatory effect on LC-NE neurons (as seen after a 2-day treatment).  Therefore, with the LC-NE neurons being under an excitatory and an inhibitory influence, the firing rate was in the range of that of the control animals. The increase in 5-HT firing activity (
Therefore, with the LC-NE neurons being under an excitatory and an inhibitory influence, the firing rate was in the range of that of the control animals. The increase in 5-HT firing activity (  ) also induced
) also induced  a tonic activation of the inhibitory postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors that may contribute to decrease the hyperactivity of the hippocampus commonly observed in patients suffering from MDD.
a tonic activation of the inhibitory postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors that may contribute to decrease the hyperactivity of the hippocampus commonly observed in patients suffering from MDD.Similar articles
-
Role of melatonin, serotonin 2B, and serotonin 2C receptors in modulating the firing activity of rat dopamine neurons.J Psychopharmacol. 2014 Feb;28(2):162-7. doi: 10.1177/0269881113510071. Epub 2013 Nov 4. J Psychopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24189440
-
Acute effects of brexpiprazole on serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine systems: an in vivo electrophysiologic characterization.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014 Dec;351(3):585-95. doi: 10.1124/jpet.114.218578. Epub 2014 Sep 15. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014. PMID: 25225185
-
Electrophysiological impact of trazodone on the dopamine and norepinephrine systems in the rat brain.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012 Jul;22(7):518-26. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2011.11.005. Epub 2011 Dec 10. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22154666
-
The roles of dopamine and serotonin, and of their receptors, in regulating sleep and waking.Prog Brain Res. 2008;172:625-46. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)00929-1. Prog Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18772053 Review.
-
Beyond the monoaminergic hypothesis: agomelatine, a new antidepressant with an innovative mechanism of action.World J Biol Psychiatry. 2009;10(2):117-26. doi: 10.1080/15622970902717024. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2009. PMID: 19255935 Review.
Cited by
-
Suspected Agomelatine-induced restless legs syndrome: a case report.BMC Psychiatry. 2021 Apr 7;21(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s12888-021-03175-5. BMC Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33827492 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine System Dysregulation in Major Depressive Disorders.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017 Dec 1;20(12):1036-1046. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyx056. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 29106542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Agomelatine: an agent against anhedonia and abulia?J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2015 Aug;122 Suppl 1:S3-7. doi: 10.1007/s00702-013-1126-6. Epub 2013 Dec 6. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2015. PMID: 24311062 Review.
-
Agomelatine, venlafaxine, and running exercise effectively prevent anxiety- and depression-like behaviors and memory impairment in restraint stressed rats.PLoS One. 2017 Nov 3;12(11):e0187671. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187671. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29099859 Free PMC article.
-
Garcinia mangostana Linn displays antidepressant-like and pro-cognitive effects in a genetic animal model of depression: a bio-behavioral study in the Flinders Sensitive Line rat.Metab Brain Dis. 2018 Apr;33(2):467-480. doi: 10.1007/s11011-017-0144-8. Epub 2017 Nov 3. Metab Brain Dis. 2018. PMID: 29101602
References
-
- Allers KA, Sharp T. Neurochemical and anatomical identification of fast-and slow-firing neurones in the rat dorsal raphe nucleus using juxtacellular labelling methods in-vivo. Neuroscience. 2003;122:193–204. - PubMed
-
- Aman TK, Shen RY, Haj-Dahmane S. D2-like dopamine receptors depolarize dorsal raphe serotonin neurons through the activation of nonselective cationic conductance. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007;320:376–385. - PubMed
-
- Audinot V, Mailliet F, Lahaye-Brasseur C, Bonnaud A, Le Gall A, Amossé C, et al. New selective ligands of human cloned melatonin MT1 and MT2 receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2003;367:553–561. - PubMed
-
- Bertaina-Anglade V, la Rochelle CD, Boyer PA, Mocaer E. Antidepressant-like effects of agomelatine (S 20098) in the learned helplessness model. Behav Pharmacol. 2006;17:703–713. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

