The Mitotic Exit Network and Cdc14 phosphatase initiate cytokinesis by counteracting CDK phosphorylations and blocking polarised growth
- PMID: 22872148
- PMCID: PMC3433788
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2012.224
The Mitotic Exit Network and Cdc14 phosphatase initiate cytokinesis by counteracting CDK phosphorylations and blocking polarised growth
Abstract
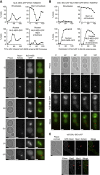
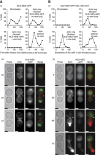
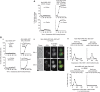
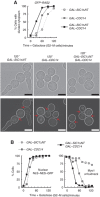
Polarisation of the actin cytoskeleton must cease during cytokinesis, to support efficient assembly and contraction of the actomyosin ring at the site of cell division, but the underlying mechanisms are still understood poorly in most species. In budding yeast, the Mitotic Exit Network (MEN) releases Cdc14 phosphatase from the nucleolus during anaphase, leading to the inactivation of mitotic forms of cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) and the onset of septation, before G1-CDK can be reactivated and drive re-polarisation of the actin cytoskeleton to a new bud. Here, we show that premature inactivation of mitotic CDK, before release of Cdc14, allows G1-CDK to divert the actin cytoskeleton away from the actomyosin ring to a new site of polarised growth, thereby delaying progression through cytokinesis. Our data indicate that cells normally avoid this problem via the MEN-dependent release of Cdc14, which counteracts all classes of CDK-mediated phosphorylations during cytokinesis and blocks polarised growth. The dephosphorylation of CDK targets is therefore central to the mechanism by which the MEN and Cdc14 initiate cytokinesis and block polarised growth during late mitosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dephosphorylation of Iqg1 by Cdc14 regulates cytokinesis in budding yeast.Mol Biol Cell. 2015 Aug 15;26(16):2913-26. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-12-1637. Epub 2015 Jun 17. Mol Biol Cell. 2015. PMID: 26085509 Free PMC article.
-
Re-examining the role of Cdc14 phosphatase in reversal of Cdk phosphorylation during mitotic exit.J Cell Sci. 2017 Aug 15;130(16):2673-2681. doi: 10.1242/jcs.201012. Epub 2017 Jun 29. J Cell Sci. 2017. PMID: 28663385
-
Studying the Role of the Mitotic Exit Network in Cytokinesis.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1505:245-262. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6502-1_18. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27826869
-
The power of MEN in cytokinesis.Cell Cycle. 2012 Jan 15;11(2):219-28. doi: 10.4161/cc.11.2.18857. Epub 2012 Jan 15. Cell Cycle. 2012. PMID: 22189712 Review.
-
Cdk-counteracting phosphatases unlock mitotic exit.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008 Dec;20(6):661-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2008.09.003. Epub 2008 Oct 22. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18845253 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Central Role of the Actomyosin Ring in Coordinating Cytokinesis Steps in Budding Yeast.J Fungi (Basel). 2024 Sep 21;10(9):662. doi: 10.3390/jof10090662. J Fungi (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39330421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cdc14 targets the Holliday junction resolvase Yen1 to the nucleus in early anaphase.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(9):1392-9. doi: 10.4161/cc.28370. Epub 2014 Mar 5. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 24626187 Free PMC article.
-
Dephosphorylation of Iqg1 by Cdc14 regulates cytokinesis in budding yeast.Mol Biol Cell. 2015 Aug 15;26(16):2913-26. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-12-1637. Epub 2015 Jun 17. Mol Biol Cell. 2015. PMID: 26085509 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of the F-BAR protein Hof1 drives septin ring splitting in budding yeast.Nat Commun. 2024 Apr 22;15(1):3383. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-47709-3. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38649354 Free PMC article.
-
TOR Complex 1: Orchestrating Nutrient Signaling and Cell Cycle Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 30;24(21):15745. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115745. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958727 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amon A, Tyers M, Futcher B, Nasmyth K (1993) Mechanisms that help the yeast cell cycle clock tick: G2 cyclins transcriptionally activate G2 cyclins and repress G1 cyclins. Cell 74: 993–1007 - PubMed
-
- Bardin AJ, Amon A (2001) MEN and SIN: what's the difference? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2: 815–826 - PubMed
-
- Barr FA, Gruneberg U (2007) Cytokinesis: placing and making the final cut. Cell 131: 847–860 - PubMed
-
- Bembenek J, Kang J, Kurischko C, Li B, Raab JR, Belanger KD, Luca FC, Yu H (2005) Crm1-mediated nuclear export of Cdc14 is required for the completion of cytokinesis in budding yeast. Cell cycle 4: 961–971 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

