Somatostatin receptor 5 and cannabinoid receptor 1 activation inhibit secretion of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide from intestinal K cells in rodents
- PMID: 22872212
- PMCID: PMC3464380
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-012-2663-5
Somatostatin receptor 5 and cannabinoid receptor 1 activation inhibit secretion of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide from intestinal K cells in rodents
Abstract
Aims/hypothesis: Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) is an enteroendocrine hormone that promotes storage of glucose and fat. Its secretion from intestinal K cells is triggered by nutrient ingestion and is modulated by intracellular cAMP. In view of the proadipogenic actions of GIP, this study aimed to identify pathways in K cells that lower cAMP levels and GIP secretion.
Methods: Murine K cells purified by flow cytometry were analysed for expression of G(αi)-coupled receptors by transcriptomic microarrays. Somatostatin and cannabinoid receptor expression was confirmed by quantitative RT-PCR. Hormone secretion in vitro was measured in GLUTag and primary murine intestinal cultures. cAMP was monitored in GLUTag cells using the genetically encoded sensor Epac2-camps. In vivo tolerance tests were performed in cannulated rats.
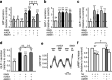
Results: Purified murine K cells expressed high mRNA levels for somatostatin receptors (Sstrs) Sstr2, Sstr3 and Sstr5, and cannabinoid receptor type 1 (Cnr1, CB1). Somatostatin inhibited GIP and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) secretion from primary small intestinal cultures, in part through SSTR5, and reduced cAMP generation in GLUTag cells. Although the CB1 agonist methanandamide (mAEA) inhibited GIP secretion, no significant effect was observed on GLP-1 secretion from primary cultures. In cannulated rats, treatment with mAEA prior to an oral glucose tolerance test suppressed plasma GIP but not GLP-1 levels, whereas the CB1 antagonist AM251 elevated basal GIP concentrations.
Conclusions/interpretation: GIP release is inhibited by somatostatin and CB1 agonists. The differential effects of CB1 ligands on GIP and GLP-1 release may provide a new tool to dissociate secretion of these incretin hormones and lower GIP but not GLP-1 levels in vivo.
Figures


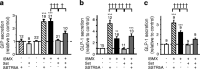


References
-
- Baggio LL, Drucker DJ (2007) Biology of incretins: GLP-1 and GIP. Gastroenterology 132:2131–2157 - PubMed
-
- Miyawaki K, Yamada Y, Ban N et al (2002) Inhibition of gastric inhibitory polypeptide signaling prevents obesity. Nat Med 8:738–742 - PubMed
-
- Irwin N, Flatt PR (2009) Evidence for beneficial effects of compromised gastric inhibitory polypeptide action in obesity-related diabetes and possible therapeutic implications. Diabetologia 52:1724–1731 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

