Association of postalimentary lipemia with atherosclerotic manifestations
- PMID: 22872287
- PMCID: PMC3854154
- DOI: 10.1590/s0100-879x2012007500127
Association of postalimentary lipemia with atherosclerotic manifestations
Abstract
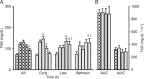
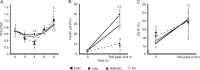
We identified different lipemic and metabolic responses after the ingestion of a standardized meal by healthy adults and related them to atherosclerotic markers. Samples from 60 normolipidemic adults were collected before and after a liquid meal (40 g fat/m² body surface) at 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 h for measurements of lipids, free fatty acids (FFA), insulin, cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP), autoantibodies to epitopes of oxidized LDL (oxLDL Ab), lipolytic activities, and apolipoprotein E polymorphism. Mean carotid intima-media thickness (cIMT) was determined by Doppler ultrasound. The volunteers were classified into early (N = 39) and late (N = 31) triacylglycerol (TAG) responders to the test meal. Late responders showed lower HDL cholesterol concentration at fasting and in the TAG peak, lower insulin and higher FFA concentrations compared to early responders. Multivariate regression analyses showed that mean cIMT was associated with gender (male) and age in early responders and by cholesterol levels at the 6th hour in late responders. oxLDL Ab were explained by lipoprotein lipase and negatively by hepatic lipase and oxLDL Ab (fasting period) by CETP (negative) and FFA (positive). This study is the first to identify a postalimentary insulin resistance state, combined with a reduced CETP response exclusively among late responders, and the identification of the regulators of postalimentary atherogenicity. Further research is required to determine the metabolic mechanisms described in the different postalimentary phenotypes observed in this study, as well as in different pathological states, as currently investigated in our laboratory.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sex-dependent variables in the modulation of postalimentary lipemia.Nutrition. 2006 Jan;22(1):9-15. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2005.05.004. Epub 2005 Oct 12. Nutrition. 2006. PMID: 16226013
-
Oxidized low-density lipoproteins and their antibodies: relationships with the reverse cholesterol transport and carotid atherosclerosis in adults without cardiovascular diseases.Clin Chim Acta. 2012 Oct 9;413(19-20):1472-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2012.05.020. Epub 2012 May 29. Clin Chim Acta. 2012. PMID: 22659061
-
A reduction of CETP activity, not an increase, is associated with modestly impaired postprandial lipemia and increased HDL-cholesterol in adult asymptomatic women.Lipids Health Dis. 2011 May 24;10:87. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-10-87. Lipids Health Dis. 2011. PMID: 21609439 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dietary fat and postprandial lipids.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2003 Nov;5(6):445-51. doi: 10.1007/s11883-003-0034-x. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2003. PMID: 14525677 Review.
-
Pharmacological modulation of cholesteryl ester transfer protein, a new therapeutic target in atherogenic dyslipidemia.Pharmacol Ther. 2004 Jan;101(1):17-38. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2003.10.001. Pharmacol Ther. 2004. PMID: 14729390 Review.
References
-
- McBride PE. Triglycerides and risk for coronary heart disease. JAMA. 2007;298:336–338. - PubMed
-
- Hokanson JE, Austin MA. Plasma triglyceride level is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease independent of highdensity lipoprotein cholesterol level: a meta-analysis of population-based prospective studies. J Cardiovasc Risk. 1996;3:213–219. - PubMed
-
- Roche HM, Gibney MJ. The impact of postprandial lipemia in accelerating atherothrombosis. J Cardiovasc Risk. 2000;7:317–324. - PubMed
-
- Bansal S, Buring JE, Rifai N, Mora S, Sacks FM, Ridker PM. Fasting compared with nonfasting triglycerides and risk of cardiovascular events in women. JAMA. 2007;298:309–316. - PubMed
-
- Nordestgaard BG, Benn M, Schnohr P, Tybjaerg-Hansen A. Nonfasting triglycerides and risk of myocardial infarction, ischemic heart disease, and death in men and women. JAMA. 2007;298:299–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

