Germ cell specification
- PMID: 22872473
- PMCID: PMC4966528
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4614-4015-4_2
Germ cell specification
Abstract
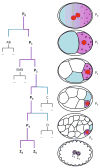
The germline of Caenorhabditis elegans derives from a single founder cell, the germline blastomere P(4). P(4) is the product of four asymmetric cleavages that divide the zygote into distinct somatic and germline (P) lineages. P(4) inherits a specialized cytoplasm ("germ plasm") containing maternally encoded proteins and RNAs. The germ plasm has been hypothesized to specify germ cell fate, but the mechanisms involved remain unclear. Three processes stand out: (1) inhibition of mRNA transcription to prevent activation of somatic development, (2) translational regulation of the nanos homolog nos-2 and of other germ plasm mRNAs, and (3) establishment of a unique, partially repressive chromatin. Together, these processes ensure that the daughters of P(4), the primordial germ cells Z2 and Z3, gastrulate inside the embryo, associate with the somatic gonad, initiate the germline transcriptional program, and proliferate during larval development to generate ∼2,000 germ cells by adulthood.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A germ cell determinant reveals parallel pathways for germ line development in Caenorhabditis elegans.Development. 2015 Oct 15;142(20):3571-82. doi: 10.1242/dev.125732. Epub 2015 Sep 22. Development. 2015. PMID: 26395476 Free PMC article.
-
Specialized germline P-bodies are required to specify germ cell fate in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos.Development. 2022 Nov 1;149(21):dev200920. doi: 10.1242/dev.200920. Epub 2022 Nov 7. Development. 2022. PMID: 36196602 Free PMC article.
-
Exclusion of germ plasm proteins from somatic lineages by cullin-dependent degradation.Nature. 2003 Aug 7;424(6949):685-9. doi: 10.1038/nature01887. Epub 2003 Jul 23. Nature. 2003. PMID: 12894212 Free PMC article.
-
Germ plasm in Caenorhabditis elegans, Drosophila and Xenopus.Dev Growth Differ. 1998 Feb;40(1):1-10. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-169x.1998.t01-4-00001.x. Dev Growth Differ. 1998. PMID: 9563905 Review.
-
Germ plasm: protein degradation in the soma.Curr Biol. 2003 Oct 28;13(21):R837-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2003.10.016. Curr Biol. 2003. PMID: 14588260 Review.
Cited by
-
The initial expansion of the C. elegans syncytial germ line is coupled to incomplete primordial germ cell cytokinesis.Development. 2021 Sep 15;148(18):dev199633. doi: 10.1242/dev.199633. Epub 2021 Jul 21. Development. 2021. PMID: 34195824 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of factors that underlie transcriptional silencing in C. elegans oocytes.PLoS Genet. 2023 Jul 21;19(7):e1010831. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010831. eCollection 2023 Jul. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 37478128 Free PMC article.
-
A twist of fate: How a meiotic protein is providing new perspectives on germ cell development.Worm. 2016 Apr 8;5(2):e1175259. doi: 10.1080/21624054.2016.1175259. eCollection 2016 Apr-Jun. Worm. 2016. PMID: 27383565 Free PMC article.
-
The Dynamic Regulation of mRNA Translation and Ribosome Biogenesis During Germ Cell Development and Reproductive Aging.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Nov 3;9:710186. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.710186. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34805139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The APC/CFZY-1/Cdc20 Complex Coordinates With OMA-1 to Regulate the Oocyte-to-Embryo Transition in Caenorhabditis elegans.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct 15;9:749654. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.749654. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34722532 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barbee SA, Lublin A, Evans TC. A novel function for the Sm proteins in germ granule localization during C. elegans embryogenesis. Curr Biol. 2002;12:1502–1506. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

