Combined PI3K/mTOR and MEK inhibition provides broad antitumor activity in faithful murine cancer models
- PMID: 22872574
- PMCID: PMC3715399
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0563
Combined PI3K/mTOR and MEK inhibition provides broad antitumor activity in faithful murine cancer models
Abstract
Purpose: Anticancer drug development is inefficient, but genetically engineered murine models (GEMM) and orthotopic, syngeneic transplants (OST) of cancer may offer advantages to in vitro and xenograft systems.
Experimental design: We assessed the activity of 16 treatment regimens in a RAS-driven, Ink4a/Arf-deficient melanoma GEMM. In addition, we tested a subset of treatment regimens in three breast cancer models representing distinct breast cancer subtypes: claudin-low (T11 OST), basal-like (C3-TAg GEMM), and luminal B (MMTV-Neu GEMM).
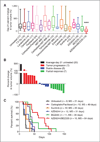
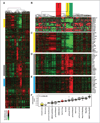
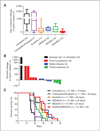
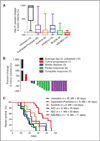
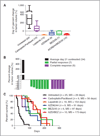
Results: Like human RAS-mutant melanoma, the melanoma GEMM was refractory to chemotherapy and single-agent small molecule therapies. Combined treatment with AZD6244 [mitogen-activated protein-extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase (MEK) inhibitor] and BEZ235 [dual phosphoinositide-3 kinase (PI3K)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor] was the only treatment regimen to exhibit significant antitumor activity, showed by marked tumor regression and improved survival. Given the surprising activity of the "AZD/BEZ" combination in the melanoma GEMM, we next tested this regimen in the "claudin-low" breast cancer model that shares gene expression features with melanoma. The AZD/BEZ regimen also exhibited significant activity in this model, leading us to testing in even more diverse GEMMs of basal-like and luminal breast cancer. The AZD/BEZ combination was highly active in these distinct breast cancer models, showing equal or greater efficacy compared with any other regimen tested in studies of over 700 tumor-bearing mice. This regimen even exhibited activity in lapatinib-resistant HER2(+) tumors.
Conclusion: These results show the use of credentialed murine models for large-scale efficacy testing of diverse anticancer regimens and predict that combinations of PI3K/mTOR and MEK inhibitors will show antitumor activity in a wide range of human malignancies.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures


References
-
- Kola I, Landis J. Can the pharmaceutical industry reduce attrition rates? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004;3:711–715. - PubMed
-
- Sharpless NE, Depinho RA. The mighty mouse: genetically engineered mouse models in cancer drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006;5:741–754. - PubMed
-
- Peterson JK, Houghton PJ. Integrating pharmacology and in vivo cancer models in preclinical and clinical drug development. Eur J Cancer. 2004;40:837–844. - PubMed
-
- Olive KP, Tuveson DA. The use of targeted mouse models for preclinical testing of novel cancer therapeutics. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:5277–5287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 GM101141/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U19 MH082441/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50-CA58223-09A1/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016086/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA148761/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA163896/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA071341/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 ES014635/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 UO1-CA141576/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 P01-ES014635/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA058223/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007040/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA141576/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA148761/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

