Filamin A is a regulator of blood-testis barrier assembly during postnatal development in the rat testis
- PMID: 22872576
- PMCID: PMC3512009
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2012-1286
Filamin A is a regulator of blood-testis barrier assembly during postnatal development in the rat testis
Abstract
The blood-testis barrier (BTB) is an important ultrastructure in the testis. A delay in its assembly during postnatal development leads to meiotic arrest. Also, a disruption of the BTB by toxicants in adult rats leads to a failure in spermatogonial differentiation. However, the regulation of BTB assembly remains unknown. Herein, filamin A, an actin filament cross-linker that is known to maintain and regulate cytoskeleton structure and function in other epithelia, was shown to be highly expressed during the assembly of Sertoli cell BTB in vitro and postnatal development of BTB in vivo, perhaps being used to maintain the actin filament network at the BTB. A knockdown of filamin A by RNA interference was found to partially perturb the Sertoli cell tight junction (TJ) permeability barrier both in vitro and in vivo. Interestingly, this down-regulating effect on the TJ barrier function after the knockdown of filamin A was associated with a mis-localization of both TJ and basal ectoplasmic specialization proteins. Filamin A knockdown also induced a disorganization of the actin filament network in Sertoli cells in vitro and in vivo. Collectively, these findings illustrate that filamin A regulates BTB assembly by recruiting these proteins to the microenvironment in the seminiferous epithelium to serve as the building blocks. In short, filamin A participates in BTB assembly by regulating protein recruitment during postnatal development in the rat testis.
Figures
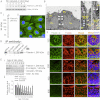


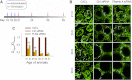
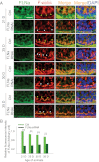

References
-
- Clermont Y, Perry B. 1957. Quantitative study of the cell population of the seminiferous tubules in immature rats. J Anat 100:241–267 - PubMed
-
- Bergmann M, Dierichs R. 1983. Postnatal formation of the blood-testis barrier in the rat with special reference to the initiation of meiosis. Anat Embryol 168:269–275 - PubMed
-
- Vitale R, Fawcett DW, Dym M. 1973. The normal development of the blood-testis barrier and the effects of clomiphene and estrogen treatment. Anat Rec 176:331–344 - PubMed
-
- Toyama Y, Ohkawa M, Oku R, Maekawa M, Yuasa S. 2001. Neonatally administered diethylstilbestrol retards the development of the blood-testis barrier in the rat. J Androl 22:413–423 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

