Combination treatment in vitro with Nutlin, a small-molecule antagonist of MDM2, and pegylated interferon-α 2a specifically targets JAK2V617F-positive polycythemia vera cells
- PMID: 22872685
- PMCID: PMC3471518
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2012-02-410712
Combination treatment in vitro with Nutlin, a small-molecule antagonist of MDM2, and pegylated interferon-α 2a specifically targets JAK2V617F-positive polycythemia vera cells
Abstract
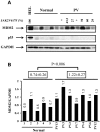
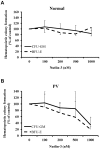
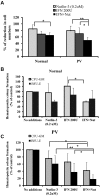
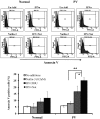
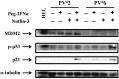
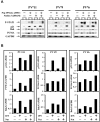
Interferon (IFN-α) is effective therapy for polycythemia vera (PV) patients, but it is frequently interrupted because of adverse events. To permit the long-term use of IFN, we propose combining low doses of IFN with Nutlin-3, an antagonist of MDM2, which is also capable of promoting PV CD34(+) cell apoptosis. Combination treatment with subtherapeutic doses of Peg IFN-α 2a and Nutlin-3 inhibited PV CD34(+) cell proliferation by 50% while inhibiting normal CD34(+) cells by 30%. Combination treatment with Nutlin-3 and Peg IFN-α 2a inhibited PV colony formation by 55%-90% while inhibiting normal colony formation by 22%-30%. The combination of these agents also decreased the proportion of JAK2V617F-positive hematopoietic progenitor cells in 6 PV patients studied. Treatment with low doses of Peg IFN-α 2a combined with Nutlin-3 increased phospho-p53 and p21 protein levels in PV CD34(+) cells and increased the degree of apoptosis. These 2 reagents affect the tumor suppressor p53 through different pathways with Peg IFN-α 2a activating p38 MAP kinase and STAT1, leading to increased p53 transcription, whereas Nutlin-3 prevents the degradation of p53. These data suggest that treatment with low doses of both Nutlin-3 combined with Peg IFN-α 2a can target PV hematopoietic progenitor cells, eliminating the numbers of malignant hematopoietic progenitor cells.
Figures
References
-
- Hoffman R, Xu M, Finazzi G, Barbui T. The polycythemias. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ Jr, Shattil SJ, et al., editors. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. Philadelphia, PA: Churchill Livingstone; 2008. pp. 1073–1108.
-
- Kralovics R, Skoda RC. Molecular pathogenesis of Philadelphia chromosome negative myeloproliferative disorders. Blood Rev. 2005;19(1):1–13. - PubMed
-
- Mesa RA. Clinical and scientific advances in the Philadelphia-chromosome negative chronic myeloproliferative disorders. Int J Hematol. 2002;76(Suppl 2):193–203. - PubMed
-
- Spivak JL. Polycythemia vera: myths, mechanisms, and management. Blood. 2002;100(13):4272–4290. - PubMed
-
- Lucet IS, Fantino E, Styles M, et al. The structural basis of Janus kinase 2 inhibition by a potent and specific pan-Janus kinase inhibitor. Blood. 2006;107(1):176–183. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

