Staphylococcus aureus leukotoxin GH promotes inflammation
- PMID: 22872735
- PMCID: PMC3448972
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jis495
Staphylococcus aureus leukotoxin GH promotes inflammation
Abstract
Background: Staphylococcus aureus produces numerous molecules that facilitate survival in the host. We recently identified a novel S. aureus leukotoxin (leukotoxin GH [LukGH]) using proteomics, but its role in virulence remains unclear. Here we investigated the role of LukGH in vivo.
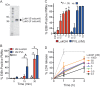
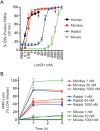
Methods: We tested cytotoxicity of LukGH toward polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) from mice, rabbits, monkeys, and humans. LukGH was administered to mice, rabbits, and a cynomolgus monkey by subcutaneous or intradermal injection to assess cytotoxicity or host response in vivo. The effects of LukGH in vivo were compared with those of Panton-Valentine leukocidin (PVL), a well-characterized S. aureus leukotoxin. The contribution of LukGH to S. aureus infection was tested using mouse and rabbit infection models.
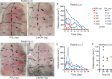
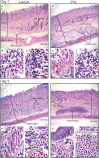
Results: Susceptibility of PMNs to LukGH was similar between humans and cynomolgus monkeys, and was greater than that of rabbits, which in turn was greater than that of mice. LukGH or PVL caused skin inflammation in rabbits and a monkey, but deletion of neither lukGH nor lukGH and lukS/F-PV reduced severity of USA300 infections in rabbits or mice. Rather, some disease parameters (eg, rabbit abscess size) were increased following infection with a lukGH and lukS/F-PV deletion strain.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that S. aureus leukotoxins enhance the host inflammatory response and influence the outcome of infection.
Figures
References
-
- Menestrina G, Dalla Serra M, Comai M, et al. Ion channels and bacterial infection: the case of β-barrel pore-forming protein toxins of Staphylococcus aureus. FEBS Lett. 2003;552:54–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

