Antisense transcription is pervasive but rarely conserved in enteric bacteria
- PMID: 22872780
- PMCID: PMC3419515
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.00156-12
Antisense transcription is pervasive but rarely conserved in enteric bacteria
Abstract
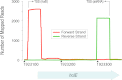
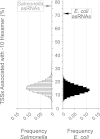
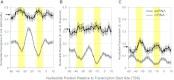
Noncoding RNAs, including antisense RNAs (asRNAs) that originate from the complementary strand of protein-coding genes, are involved in the regulation of gene expression in all domains of life. Recent application of deep-sequencing technologies has revealed that the transcription of asRNAs occurs genome-wide in bacteria. Although the role of the vast majority of asRNAs remains unknown, it is often assumed that their presence implies important regulatory functions, similar to those of other noncoding RNAs. Alternatively, many antisense transcripts may be produced by chance transcription events from promoter-like sequences that result from the degenerate nature of bacterial transcription factor binding sites. To investigate the biological relevance of antisense transcripts, we compared genome-wide patterns of asRNA expression in closely related enteric bacteria, Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, by performing strand-specific transcriptome sequencing. Although antisense transcripts are abundant in both species, less than 3% of asRNAs are expressed at high levels in both species, and only about 14% appear to be conserved among species. And unlike the promoters of protein-coding genes, asRNA promoters show no evidence of sequence conservation between, or even within, species. Our findings suggest that many or even most bacterial asRNAs are nonadaptive by-products of the cell's transcription machinery. IMPORTANCE Application of high-throughput methods has revealed the expression throughout bacterial genomes of transcripts encoded on the strand complementary to protein-coding genes. Because transcription is costly, it is usually assumed that these transcripts, termed antisense RNAs (asRNAs), serve some function; however, the role of most asRNAs is unclear, raising questions about their relevance in cellular processes. Because natural selection conserves functional elements, comparisons between related species provide a method for assessing functionality genome-wide. Applying such an approach, we assayed all transcripts in two closely related bacteria, Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, and demonstrate that, although the levels of genome-wide antisense transcription are similarly high in both bacteria, only a small fraction of asRNAs are shared across species. Moreover, the promoters associated with asRNAs show no evidence of sequence conservation between, or even within, species. These findings indicate that despite the genome-wide transcription of asRNAs, many of these transcripts are likely nonfunctional.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

