Measurement of Hymenoptera venom specific IgE by the IMMULITE 3gAllergy in subjects with negative or positive results by ImmunoCAP
- PMID: 22872822
- PMCID: PMC3406299
- DOI: 10.5415/apallergy.2012.2.3.195
Measurement of Hymenoptera venom specific IgE by the IMMULITE 3gAllergy in subjects with negative or positive results by ImmunoCAP
Erratum in
- Asia Pac Allergy. 2013 Jan;3(1):74
Abstract
Background: Patients may receive negative results from a specific IgE (sIgE) test such as the ImmunoCAP (CAP) despite a documented history of systemic reaction to a Hymenoptera sting. Thus, further testing may be required using another serological method or venom skin prick tests to confirm allergy diagnosis and correct species.
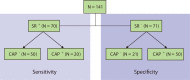
Objective: To evaluate the sensitivity and the specificity of CAP and IMMULITE 3gAllergy (IMMULITE) for detecting sIgE to Paper wasp (WA) and Yellow Jacket (YJ) venoms using patient clinical history as the comparator.
Methods: Sera from 70 participants with a history of systemic reactions (SR) to WA and/or YJ stings were tested using CAP and IMMULITE. Fifty participants from this group had negative results on CAP. To assess specificity, sera from 71 participants who had never experienced either a WA or YJ sting were tested using CAP and IMMULITE. Fifty participants from this group tested positive using CAP.
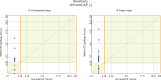
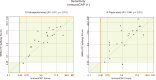
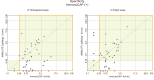
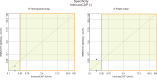
Results: In participants with a history of systemic reaction to a Hymenoptera sting, yet who tested negative for WA and/or YJ sIgE according to CAP, the positivity rate according to IMMULITE was 20-42% using 0.10 IU(A)/mL as the limit of detection (LoD), per the manufacturer's specification. When the LoD for CAP (0.35 IU(A)/mL) was applied to the IMMULITE results, positivity according to IMMULITE was 14-26%. Overall, sensitivity, specificity, and agreement with SR were greater for IMMULITE than for CAP. For YJ: sensitivity (IMMULITE:CAP), 42.8%:28.5%; specificity, 53.5%:39.4%; agreement, 48.2%:34%. For WA, sensitivity (IMMULITE:CAP), 58.6%:28.5%; specificity, 49.3%:47.8%; agreement, 43.9%:38.3%.
Conclusion: The IMMULITE performed well for detecting sIgE to Hymenoptera venom.
Keywords: Allergy; IMMULITE; ImmunoCAP; Sensitivity; Specificity; Venom specific IgE.
Figures
References
-
- Plebani M, Borghesan F, Faggian D. Clinical efficiency of in vitro and in vivo tests for allergic diseases. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1995;74:23–28. - PubMed
-
- Shoji J, Kato H, Kitazawa M, Inada N, Sawa M. Evaluation of staphylococcal enterotoxin-specific IgE antibody in tears in allergic keratoconjunctival disorders. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2003;47:609–611. - PubMed
-
- Ogino S, Bessho K, Harada T, Irifune M, Matsunaga T. Evaluation of allergen-specific IgE antibodies by MAST for the diagnosis of nasal allergy. Rhinology. 1993;31:27–31. - PubMed
-
- Nakagawa T, Miyamoto T, Akiyama K, Takasaka T, Kobayashi S, Nakazawa T, Ito K, Iikura Y, Baba M, Okuda M. Evaluation of allergen-specific IgE antibody and total IgE with a new IgE detection system named FAST: fluorescence allergosorbent test. Arerugi. 1992;41:93–105. - PubMed
-
- Sabbah A, Langlois P. The Pharmacia CAP system as a new measure of specific IgE. Application in the diagnosis of hypersensitivity to the venom of the Vespula wasp. Allerg Immunol (Paris) 1990;22:173–178. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
