Anterior cranial base reconstruction with a reverse temporalis muscle flap and calvarial bone graft
- PMID: 22872838
- PMCID: PMC3408280
- DOI: 10.5999/aps.2012.39.4.345
Anterior cranial base reconstruction with a reverse temporalis muscle flap and calvarial bone graft
Abstract
Background: Cranial base defects are challenging to reconstruct without serious complications. Although free tissue transfer has been used widely and efficiently, it still has the limitation of requiring a long operation time along with the burden of microanastomosis and donor site morbidity. We propose using a reverse temporalis muscle flap and calvarial bone graft as an alternative option to a free flap for anterior cranial base reconstruction.
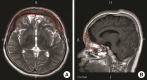
Methods: Between April 2009 and February 2012, cranial base reconstructions using an autologous calvarial split bone graft combined with a reverse temporalis muscle flap were performed in five patients. Medical records were retrospectively analyzed and postoperative computed tomography scans, magnetic resonance imaging, and angiography findings were examined to evaluate graft survival and flap viability.
Results: The mean follow-up period was 11.8 months and the mean operation time for reconstruction was 8.4±3.36 hours. The defects involved the anterior cranial base, including the orbital roof and the frontal and ethmoidal sinus. All reconstructions were successful. Viable flap vascularity and bone survival were observed. There were no serious complications except for acceptable donor site depressions, which were easily corrected with minor procedures.
Conclusions: The reverse temporalis muscle flap could provide sufficient bulkiness to fill dead space and sufficient vascularity to endure infection. The calvarial bone graft provides a rigid framework, which is critical for maintaining the cranial base structure. Combined anterior cranial base reconstruction with a reverse temporalis muscle flap and calvarial bone graft could be a viable alternative to free tissue transfer.
Keywords: Bone transplantation; Skull base; Surgical flaps.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A combined reverse temporalis muscle flap and pericranial flap for reconstruction of an anterior cranial base defect: a case report.Ann Plast Surg. 1997 Aug;39(2):190-2. doi: 10.1097/00000637-199708000-00014. Ann Plast Surg. 1997. PMID: 9262775
-
Temporalis myofascial flap for primary cranial base reconstruction after tumor resection.Skull Base. 2008 Jul;18(4):253-63. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1016958. Skull Base. 2008. PMID: 19119340 Free PMC article.
-
Reverse U-shaped split temporalis musculofascial flap in cranial base reconstruction.Ann Plast Surg. 1999 Jun;42(6):644-50. doi: 10.1097/00000637-199906000-00011. Ann Plast Surg. 1999. PMID: 10382802
-
[Cranio-facial resections].Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 1990 Jan-Feb;10(1):27-48. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 1990. PMID: 2203220 Review. Italian.
-
Autologous Temporalis Subfascial Fat Graft for Skull Base Repair: A Novel Technique.Oper Neurosurg. 2021 Mar 15;20(4):E274-E278. doi: 10.1093/ons/opaa442. Oper Neurosurg. 2021. PMID: 33469665 Review.
Cited by
-
Extended temporalis flap for skull base reconstruction.Arch Craniofac Surg. 2019 Apr;20(2):126-129. doi: 10.7181/acfs.2018.02278. Epub 2019 Apr 20. Arch Craniofac Surg. 2019. PMID: 31048650 Free PMC article.
-
Dural reconstruction with or without a bone graft of paranasal and anterior skullbase malignancies: Retrospective single-center analysis of 11 cases and review of literature.Brain Spine. 2023 Dec 30;4:102740. doi: 10.1016/j.bas.2023.102740. eCollection 2024. Brain Spine. 2023. PMID: 38510629 Free PMC article.
-
Anterior skull base reconstruction using an anterolateral thigh free flap.Arch Craniofac Surg. 2021 Oct;22(5):232-238. doi: 10.7181/acfs.2021.00290. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Arch Craniofac Surg. 2021. PMID: 34732034 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smith JE, Ducic Y, Adelson RT. Temporalis muscle flap for reconstruction of skull base defects. Head Neck. 2010;32:199–203. - PubMed
-
- Califano J, Cordeiro PG, Disa JJ, et al. Anterior cranial base reconstruction using free tissue transfer: changing trends. Head Neck. 2003;25:89–96. - PubMed
-
- Boyle JO, Shah KC, Shah JP. Craniofacial resection for malignant neoplasms of the skull base: an overview. J Surg Oncol. 1998;69:275–284. - PubMed
-
- Gagliardi F, Boari N, Mortini P. Reconstruction techniques in skull base surgery. J Craniofac Surg. 2011;22:1015–1020. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

