Keap1 degradation by autophagy for the maintenance of redox homeostasis
- PMID: 22872865
- PMCID: PMC3427110
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1121572109
Keap1 degradation by autophagy for the maintenance of redox homeostasis
Abstract
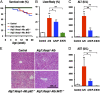
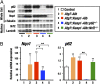
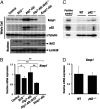
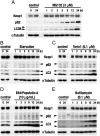
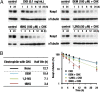
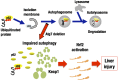
The Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1)-NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) system is essential for cytoprotection against oxidative and electrophilic insults. Under unstressed conditions, Keap1 serves as an adaptor for ubiquitin E3 ligase and promotes proteasomal degradation of Nrf2, but Nrf2 is stabilized when Keap1 is inactivated under oxidative/electrophilic stress conditions. Autophagy-deficient mice show aberrant accumulation of p62, a multifunctional scaffold protein, and develop severe liver damage. The p62 accumulation disrupts the Keap1-Nrf2 association and provokes Nrf2 stabilization and accumulation. However, individual contributions of p62 and Nrf2 to the autophagy-deficiency-driven liver pathogenesis have not been clarified. To examine whether Nrf2 caused the liver injury independent of p62, we crossed liver-specific Atg7::Keap1-Alb double-mutant mice into p62- and Nrf2-null backgrounds. Although Atg7::Keap1-Alb::p62(-/-) triple-mutant mice displayed defective autophagy accompanied by the robust accumulation of Nrf2 and severe liver injury, Atg7::Keap1-Alb::Nrf2(-/-) triple-mutant mice did not show any signs of such hepatocellular damage. Importantly, in this study we noticed that Keap1 accumulated in the Atg7- or p62-deficient mouse livers and the Keap1 level did not change by a proteasome inhibitor, indicating that the Keap1 protein is constitutively degraded through the autophagy pathway. This finding is in clear contrast to the Nrf2 degradation through the proteasome pathway. We also found that treatment of cells with tert-butylhydroquinone accelerated the Keap1 degradation. These results thus indicate that Nrf2 accumulation is the dominant cause to provoke the liver damage in the autophagy-deficient mice. The autophagy pathway maintains the integrity of the Keap1-Nrf2 system for the normal liver function by governing the Keap1 turnover.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Itoh K, et al. Keap1 regulates both cytoplasmic-nuclear shuttling and degradation of Nrf2 in response to electrophiles. Genes Cells. 2003;8:379–391. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi A, Ohta T, Yamamoto M. Unique function of the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway in the inducible expression of antioxidant and detoxifying enzymes. Methods Enzymol. 2004;378:273–286. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi M, Yamamoto M. Molecular mechanisms activating the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway of antioxidant gene regulation. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2005;7:385–394. - PubMed
-
- Motohashi H, Yamamoto M. Nrf2-Keap1 defines a physiologically important stress response mechanism. Trends Mol Med. 2004;10:549–557. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

