Direct sampling of cystic fibrosis lungs indicates that DNA-based analyses of upper-airway specimens can misrepresent lung microbiota
- PMID: 22872870
- PMCID: PMC3427132
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1107435109
Direct sampling of cystic fibrosis lungs indicates that DNA-based analyses of upper-airway specimens can misrepresent lung microbiota
Abstract
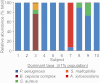
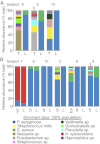
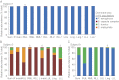
Recent work using culture-independent methods suggests that the lungs of cystic fibrosis (CF) patients harbor a vast array of bacteria not conventionally implicated in CF lung disease. However, sampling lung secretions in living subjects requires that expectorated specimens or collection devices pass through the oropharynx. Thus, contamination could confound results. Here, we compared culture-independent analyses of throat and sputum specimens to samples directly obtained from the lungs at the time of transplantation. We found that CF lungs with advanced disease contained relatively homogenous populations of typical CF pathogens. In contrast, upper-airway specimens from the same subjects contained higher levels of microbial diversity and organisms not typically considered CF pathogens. Furthermore, sputum exhibited day-to-day variation in the abundance of nontypical organisms, even in the absence of clinical changes. These findings suggest that oropharyngeal contamination could limit the accuracy of DNA-based measurements on upper-airway specimens. This work highlights the importance of sampling procedures for microbiome studies and suggests that methods that account for contamination are needed when DNA-based methods are used on clinical specimens.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Emerson J, McNamara S, Buccat AM, Worrell K, Burns JL. Changes in cystic fibrosis sputum microbiology in the United States between 1995 and 2008. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2010;45:363–370. - PubMed
-
- Klepac-Ceraj V, et al. Relationship between cystic fibrosis respiratory tract bacterial communities and age, genotype, antibiotics and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Environ Microbiol. 2010;12:1293–1303. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

