Risk assessment in sepsis: a new prognostication rule by APACHE II score and serum soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor
- PMID: 22873681
- PMCID: PMC3580738
- DOI: 10.1186/cc11463
Risk assessment in sepsis: a new prognostication rule by APACHE II score and serum soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor
Abstract
Introduction: Early risk assessment is the mainstay of management of patients with sepsis. APACHE II is the gold standard prognostic stratification system. A prediction rule that aimed to improve prognostication by APACHE II with the application of serum suPAR (soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor) is developed.
Methods: A prospective study cohort enrolled 1914 patients with sepsis including 62.2% with sepsis and 37.8% with severe sepsis/septic shock. Serum suPAR was measured in samples drawn after diagnosis by an enzyme-immunoabsorbent assay; in 367 patients sequential measurements were performed. After ROC analysis and multivariate logistic regression analysis a prediction rule for risk was developed. The rule was validated in a double-blind fashion by an independent confirmation cohort of 196 sepsis patients, predominantly severe sepsis/septic shock patients, from Sweden.
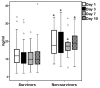
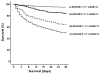
Results: Serum suPAR remained stable within survivors and non-survivors for 10 days. Regression analysis showed that APACHE II ≥ 17 and suPAR ≥ 12 ng/ml were independently associated with unfavorable outcome. Four strata of risk were identified: i) APACHE II <17 and suPAR <12 ng/ml with mortality 5.5%; ii) APACHE II < 17 and suPAR ≥ 12 ng/ml with mortality 17.4%; iii) APACHE II ≥ 17 and suPAR <12 ng/ml with mortality 37.4%; and iv) APACHE II ≥ 17 and suPAR ≥ 12 ng/ml with mortality 51.7%. This prediction rule was confirmed by the Swedish cohort.
Conclusions: A novel prediction rule with four levels of risk in sepsis based on APACHE II score and serum suPAR is proposed. Prognostication by this rule is confirmed by an independent cohort.
Figures


References
-
- Ostrowski SR, Piironen T, Hoyer-Hansen G, Gerstoft J, Pedersen BK, Ullum H. High plasma levels of intact and cleaved soluble urokinase receptor reflect immune activation and are independent predictors of mortality in HIV-1-infected patients. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2005;39:23–31. doi: 10.1097/01.qai.0000157950.02076.a6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sidenius N, Sier CF, Ullum H, Pedersen BK, Lepri AC, Blasi F, Eugen-Olsen J. Serum level of soluble urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor is a strong and independent predictor of survival in human immunodeficiency virus infection. Blood. 2000;96:4091–4095. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

