Wnt1 inducible signaling pathway protein 1 (WISP1) targets PRAS40 to govern β-amyloid apoptotic injury of microglia
- PMID: 22873724
- PMCID: PMC3521866
- DOI: 10.2174/156720212803530618
Wnt1 inducible signaling pathway protein 1 (WISP1) targets PRAS40 to govern β-amyloid apoptotic injury of microglia
Abstract
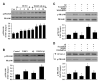
Given the present challenges to attain effective treatment for β-amyloid (Aβ) toxicity in neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, development of novel cytoprotective pathways that can assist immune mediated therapies through the preservation of central nervous system microglia could offer significant promise. We show that the CCN4 protein, Wnt1 inducible signaling pathway protein 1 (WISP1), is initially up-regulated by Aβ and can modulate its endogenous expression for the protection of microglia during Aβ mediated apoptosis. WISP1 activates mTOR and phosphorylates p70S6K and 4EBP1 through the control of the regulatory mTOR component PRAS40. Loss of PRAS40 through gene reduction or inhibition by WISP1 is cytoprotective. WISP1 ultimately governs PRAS40 by sequestering PRAS40 intracellularly through post-translational phosphorylation and binding to protein 14-3-3. Our work identifies WISP1, mTOR signaling, and PRAS40 as targets for new strategies directed against Alzheimer's disease and related disorders.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tuberous sclerosis protein 2 (TSC2) modulates CCN4 cytoprotection during apoptotic amyloid toxicity in microglia.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2013 Feb;10(1):29-38. doi: 10.2174/156720213804806007. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2013. PMID: 23244622 Free PMC article.
-
CCN4/WISP1 (WNT1 inducible signaling pathway protein 1): a focus on its role in cancer.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015 May;62:142-6. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2015.03.007. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25794425 Review.
-
WISP1: Clinical insights for a proliferative and restorative member of the CCN family.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2014;11(4):378-89. doi: 10.2174/1567202611666140912115107. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2014. PMID: 25219658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
WISP1 (CCN4) autoregulates its expression and nuclear trafficking of β-catenin during oxidant stress with limited effects upon neuronal autophagy.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2012 May;9(2):91-101. doi: 10.2174/156720212800410858. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2012. PMID: 22475393 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of long non-coding RNA SNHG14 protects against acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide through microRNA-34c-3p-dependent inhibition of WISP1.Respir Res. 2019 Oct 28;20(1):233. doi: 10.1186/s12931-019-1207-7. Respir Res. 2019. PMID: 31660971 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
WISP1 Is Involved in the Pathogenesis of Kashin-Beck Disease via the Autophagy Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 7;24(22):16037. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216037. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003226 Free PMC article.
-
Novel applications of trophic factors, Wnt and WISP for neuronal repair and regeneration in metabolic disease.Neural Regen Res. 2015 Apr;10(4):518-28. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.155427. Neural Regen Res. 2015. PMID: 26170801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) and the silent mating-type information regulation 2 homolog 1 (SIRT1): oversight for neurodegenerative disorders.Biochem Soc Trans. 2018 Apr 17;46(2):351-360. doi: 10.1042/BST20170121. Epub 2018 Mar 9. Biochem Soc Trans. 2018. PMID: 29523769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stem cell guidance through the mechanistic target of rapamycin.World J Stem Cells. 2015 Aug 26;7(7):999-1009. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i7.999. World J Stem Cells. 2015. PMID: 26328016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cognitive Impairment in Multiple Sclerosis.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Jul 23;10(7):871. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10070871. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37508898 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Macsai CE, Georgiou KR, Foster BK, Zannettino AC, Xian CJ. Microarray expression analysis of genes and pathways involved in growth plate cartilage injury responses and bony repair. Bone. 2012 May;50(5):1081–91. - PubMed
-
- Colston JT, de la Rosa SD, Koehler M, Gonzales K, Mestril R, Freeman GL, et al. Wnt-induced secreted protein-1 is a prohypertrophic and profibrotic growth factor. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007 Sep;293(3):H1839–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
