Utility of Procalcitonin (PCT) and Mid regional pro-Adrenomedullin (MR-proADM) in risk stratification of critically ill febrile patients in Emergency Department (ED). A comparison with APACHE II score
- PMID: 22874067
- PMCID: PMC3447640
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-12-184
Utility of Procalcitonin (PCT) and Mid regional pro-Adrenomedullin (MR-proADM) in risk stratification of critically ill febrile patients in Emergency Department (ED). A comparison with APACHE II score
Abstract
Background: The aim of our study was to evaluate the prognostic value of MR-proADM and PCT levels in febrile patients in the ED in comparison with a disease severity index score, the APACHE II score. We also evaluated the ability of MR-proADM and PCT to predict hospitalization.
Methods: This was an observational, multicentric study. We enrolled 128 patients referred to the ED with high fever and a suspicion of severe infection such as sepsis, lower respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, gastrointestinal infections, soft tissue infections, central nervous system infections, or osteomyelitis. The APACHE II score was calculated for each patient.
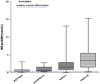
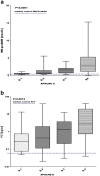
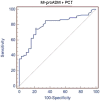
Results: MR-proADM median values in controls were 0.5 nmol/l as compared with 0.85 nmol/l in patients (P < 0.0001), while PCT values in controls were 0.06 ng/ml versus 0.56 ng/ml in patients (P < 0.0001). In all patients there was a statistically significant stepwise increase in MR-proADM levels in accordance with PCT values (P < 0.0001). MR-proADM and PCT levels were significantly increased in accordance with the Apache II quartiles (P < 0.0001 and P = 0.0012 respectively).In the respiratory infections, urinary infections, and sepsis-septic shock groups we found a correlation between the Apache II and MR-proADM respectively and MR-proADM and PCT respectively. We evaluated the ability of MR-proADM and PCT to predict hospitalization in patients admitted to our emergency departments complaining of fever. MR-proADM alone had an AUC of 0.694, while PCT alone had an AUC of 0.763. The combined use of PCT and MR-proADM instead showed an AUC of 0.79.
Conclusions: The present study highlights the way in which MR-proADM and PCT may be helpful to the febrile patient's care in the ED. Our data support the prognostic role of MR-proADM and PCT in that setting, as demonstrated by the correlation with the APACHE II score. The combined use of the two biomarkers can predict a subsequent hospitalization of febrile patients. The rational use of these two molecules could lead to several advantages, such as faster diagnosis, more accurate risk stratification, and optimization of the treatment, with consequent benefit to the patient and considerably reduced costs.
Figures

References
-
- Limper M, Eeftinck Schattenkerk D, de Kruif MD, van Wissen M, Brandjes DP, Duits AJ, van Gorp EC. One-year epidemiology of fever at the Emergency Department. Neth J Med. 2011;69:124–128. - PubMed
-
- Schuetz P, Christ-Crain M, Thomann R, Falconnier C, Wolbers M, Widmer I, Neidert S, Fricker T, Blum C, Schild U, Regez K, Schoenenberger R, Henzen C, Bregenzer T, Hoess C, Krause M, Bucher HC, Zimmerli W, Mueller B. ProHOSP Study Group. Effect of procalcitonin-based guidelines vs standard guidelines on antibiotic use in lower respiratory tract infections: the ProHOSP randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2009;9:1059–1066. - PubMed
-
- Bone RC, Balk RA, Cerra FB, Dellinger RP, Fein AM, Knaus WA, Schein RM, Sibbald WJ. ACCP/SCCM consensus conference committee. Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. The ACCP/SCCM consensus conference committee. American college of chest physicians/society of critical care medicine. 1992. Chest. 2009;136:e28. doi: 10.1378/chest.09-2267. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bossink AW, Groeneveld AB, Thijs LG. Prediction of microbial infection and mortality in medical patients with fever: plasma procalcitonin, neutrophilic elastase-alpha1-antitrypsin, and lactoferrin compared with clinical variables. Clin Infect Dis. 1999;29:398–407. doi: 10.1086/520222. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

