Intrinsic properties of the sodium sensor neurons in the rat median preoptic nucleus
- PMID: 22874426
- PMCID: PMC3469662
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00260.2012
Intrinsic properties of the sodium sensor neurons in the rat median preoptic nucleus
Abstract
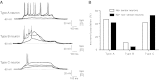
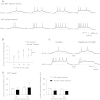
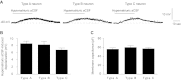
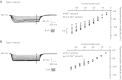
The essential role of the median preoptic nucleus (MnPO) in the integration of chemosensory information associated with the hydromineral state of the rat relies on the presence of a unique population of sodium (Na+) sensor neurons. Little is known about the intrinsic properties of these neurons; therefore, we used whole cell recordings in acute brain slices to determine the electrical fingerprints of this specific neural population of rat MnPO. The data collected from a large sample of neurons (115) indicated that the Na+ sensor neurons represent a majority of the MnPO neurons in situ (83%). These neurons displayed great diversity in both firing patterns induced by transient depolarizing current steps and rectifying properties activated by hyperpolarizing current steps. This diversity of electrical properties was also present in non-Na+ sensor neurons. Subpopulations of Na+ sensor neurons could be distinguished, however, from the non-Na+ sensor neurons. The firing frequency was higher in Na+ sensor neurons, showing irregular spike discharges, and the amplitude of the time-dependent rectification was weaker in the Na+ sensor neurons than in non-Na+ sensor neurons. The diversity among the electrical properties of the MnPO neurons contrasts with the relative function homogeneity (Na+ sensing). However, this diversity might be correlated with a variety of direct synaptic connections linking the MnPO to different brain areas involved in various aspects of the restoration and conservation of the body fluid homeostasis.
Figures
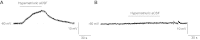

References
-
- Aradachi H, Honda K, Negoro H, Kubota T. Median preoptic neurones projecting to the supraoptic nucleus are sensitive to haemodynamic changes as well as to rise in plasma osmolality in rats. J Neuroendocrinol 8: 35–43, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Bai D, Renaud LP. ANG II AT1 receptors induce depolarization and inward current in rat median preoptic neurons in vitro. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 275: R632–R639, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Blatz AL, Magleby KL. Single apamin-blocked Ca-activated K+ channels of small conductance in cultured rat skeletal muscle. Nature 323: 718–720, 1986 - PubMed
-
- Bodnar RJ, Glass MJ, Ragnauth A, Cooper ML. General, mu and kappa opioid antagonists in the nucleus accumbens alter food intake under deprivation, glucoprivic and palatable conditions. Brain Res 66: 205–212, 1995 - PubMed
-
- Brown DR, Holtzman SG. Opiate antagonists: central sites of action in suppressing water intake of the rat. Brain Res 221: 432–436, 1981 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

