Inactivation of the Cullin (CUL)-RING E3 ligase by the NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 triggers protective autophagy in cancer cells
- PMID: 22874562
- PMCID: PMC3494597
- DOI: 10.4161/auto.21484
Inactivation of the Cullin (CUL)-RING E3 ligase by the NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 triggers protective autophagy in cancer cells
Abstract
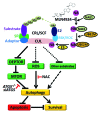
The multiunit Cullin (CUL)-RING E3 ligase (CRL) controls diverse biological processes by targeting a mass of substrates for ubiquitination and degradation, whereas its dysfunction causes carcinogenesis. Post-translational neddylation of CUL, a process triggered by the NEDD8-activating enzyme E1 subunit 1 (NAE1), is required for CRL activation. Recently, MLN4924 was discovered via a high-throughput screen as a specific NAE1 inhibitor and first-in-class anticancer drug. By blocking CUL neddylation, MLN4924 inactivates CRL and causes the accumulation of CRL substrates that trigger cell cycle arrest, senescence and/or apoptosis to suppress the growth of cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Recently, we found that MLN4924 also triggers protective autophagy in response to CRL inactivation. MLN4924-induced autophagy is attributed partially to the inhibition of mechanistic target of rapamycin (also known as mammalian target of rapamycin, MTOR) activity by the accumulation of the MTOR inhibitory protein DEPTOR, as well as reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced stress. Moreover, the blockage of autophagy response enhances apoptosis in MLN4924-treated cells. Together, our findings not only reveal autophagy as a novel cellular response to CRL inactivation by MLN4924, but also provide a piece of proof-of-concept evidence for the combination of MLN4924 with autophagy inhibitors to enhance therapeutic efficacy.
Keywords: Cullin-RING E3 ligase; DEPTOR; MLN4924; MTOR; NEDD8-activating enzyme; SKP1-Cullin-F-box (SCF) E3 ligase; autophagy; neddylation.
Figures
Comment on
- Luo Z, Yu G, Lee HW, Li L, Wang L, Yang D, et al. The Nedd8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 induces autophagy and apoptosis to suppress liver cancer cell growth. Cancer Res. 2012;72:3360–71. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-0388.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
