Autophagy is a protective response to ethanol neurotoxicity
- PMID: 22874567
- PMCID: PMC3494588
- DOI: 10.4161/auto.21376
Autophagy is a protective response to ethanol neurotoxicity
Abstract
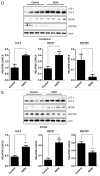
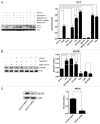
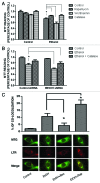
Ethanol is a neuroteratogen and neurodegeneration is the most devastating consequence of developmental exposure to ethanol. The mechanisms underlying ethanol-induced neurodegeneration are complex. Ethanol exposure produces reactive oxygen species (ROS) which cause oxidative stress in the brain. We hypothesized that ethanol would activate autophagy to alleviate oxidative stress and neurotoxicity. Our results indicated that ethanol increased the level of the autophagic marker Map1lc3-II (LC3-II) and upregulated LC3 puncta in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. It also enhanced the levels of LC3-II and BECN1 in the developing brain; meanwhile, ethanol reduced SQSTM1 (p62) levels. Bafilomycin A(1), an inhibitor of autophagosome and lysosome fusion, increased p62 levels in the presence of ethanol. Bafilomycin A(1) and rapamycin potentiated ethanol-increased LC3 lipidation, whereas wortmannin and a BECN1-specific shRNA inhibited ethanol-promoted LC3 lipidation. Ethanol increased mitophagy, which was also modulated by BECN1 shRNA and rapamycin. The evidence suggested that ethanol promoted autophagic flux. Activation of autophagy by rapamycin reduced ethanol-induced ROS generation and ameliorated ethanol-induced neuronal death in vitro and in the developing brain, whereas inhibition of autophagy by wortmannin and BECN1-specific shRNA potentiated ethanol-induced ROS production and exacerbated ethanol neurotoxicity. Furthermore, ethanol inhibited the MTOR pathway and downregulation of MTOR offered neuroprotection. Taken together, the results suggest that autophagy activation is a neuroprotective response to alleviate ethanol toxicity. Ethanol modulation of autophagic activity may be mediated by the MTOR pathway.
Keywords: alcohol; cerebellum; cerebral cortex; fetal alcohol spectrum disorders; mitophagy; neurodegeneration.
Figures






References
-
- Riley EP, McGee CL. Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders: an overview with emphasis on changes in brain and behavior. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2005;230:357–65. - PubMed
-
- Yang C, Han LO. Knockdown of Beclin 1 inhibits vitamin K3‑induced autophagy, but promotes apoptosis of human hepatoma SMMC-7721 cells. Mol Med Report. 2010;3:801–7. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Gibson SB. Is mitochondrial generation of reactive oxygen species a trigger for autophagy? Autophagy. 2008;4:246–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
