Role of A1 receptors in renal sympathetic neurotransmission in the mouse kidney
- PMID: 22874760
- PMCID: PMC3469685
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00363.2012
Role of A1 receptors in renal sympathetic neurotransmission in the mouse kidney
Abstract
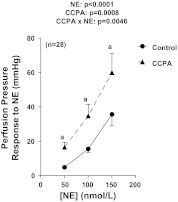
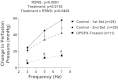
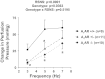
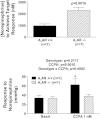
A(1) receptors may participate in renal sympathetic neurotransmission by enhancing the postjunctional effects of norepinephrine. The purpose of this study was to test this concept using A(1) receptor knockout (A(1)AR-/-) mice. In isolated kidneys from nontransgenic mice perfused with Tyrode's solution at a constant rate, renal sympathetic nerve stimulation (RSNS) increased (P < 0.0001) renal venous perfusate levels of inosine (adenosine metabolite) from 23.9 ± 3.7 to 32.7 ± 5.1, 68.2 ± 12.4, and 94.0 ± 14.3 ng/ml at 3, 5, and 7 Hz, respectively (n = 28), suggesting frequency-dependent production of adenosine. Conversely, RSNS decreased (P < 0.0001) renal venous perfusate levels of 5'-AMP (adenosine precursor) from 1.4 ± 0.3 to 1.1 ± 0.3, 0.80 ± 0.2, and 0.6 ± 0.2 ng/ml at 3, 5, and 7 Hz, respectively (n = 28), suggesting frequency-dependent increased metabolism of 5'-AMP. In kidneys from nontransgenic mice, blockade of adenosine receptors with 1,3-dipropyl-8-p-sulfophenylxanthine attenuated (P = 0.0130) vasoconstrictor responses to RSNS at 3, 5, and 7 Hz [control (n = 29): 22 ± 4, 34 ± 6, 42 ± 6 mmHg, respectively; 1,3-dipropyl-8-p-sulfophenylxanthine-treated (n = 11): 6 ± 1, 12 ± 3, 15 ± 3 mmHg, respectively]. In A(1)AR-/- kidneys (n = 10), vasoconstrictor responses to RSNS at 3, 5, and 7 Hz were 7 ± 3, 20 ± 5, and 36 ± 9 mmHg, respectively. In kidneys from wild-type littermates (n = 9), responses were 27 ± 9, 58 ± 14, and 59 ± 11 mmHg, respectively (effect of genotype: P = 0.0363). In kidneys from nontransgenic mice, 2-chloro-N(6)-cyclopentyladenosine (CCPA; highly selective A(1) receptor agonist) increased renal vasoconstriction induced by norepinephrine (P = 0.0008; n = 28). In kidneys from A(1)AR-/- the response to norepinephrine was attenuated and the ability of CCPA to enhance responses to norepinephrine was abolished. In conclusion, adenosine formed during RSNS enhances the postjunctional effects of released norepinephrine by activating A(1) receptors.
Figures
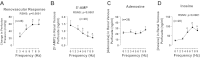
Similar articles
-
Role of CD73 in Renal Sympathetic Neurotransmission in the Mouse Kidney.Physiol Rep. 2013 Aug 20;1(3):e00057. doi: 10.1002/phy2.57. Physiol Rep. 2013. PMID: 24066228 Free PMC article.
-
Alkaline Phosphatase Inhibitors Attenuate Renovascular Responses to Norepinephrine.Hypertension. 2017 Mar;69(3):484-493. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.116.08623. Epub 2017 Jan 30. Hypertension. 2017. PMID: 28137984 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous adenosine contributes to renal sympathetic neurotransmission via postjunctional A1 receptor-mediated coincident signaling.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012 Feb 15;302(4):F466-76. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00495.2011. Epub 2011 Nov 23. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22114202 Free PMC article.
-
Presynaptic inhibition of sympathetic neurotransmission by adenosine in the rat kidney.Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Dec 17;76(4):301-7. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90100-x. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981. PMID: 6276189
-
Assessment of nerve stimulation-induced release of purines from mouse kidneys by tandem mass spectrometry.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008 Jun;325(3):920-6. doi: 10.1124/jpet.108.137752. Epub 2008 Mar 5. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008. PMID: 18322147
Cited by
-
Adenosine Receptors Influence Hypertension in Dahl Salt-Sensitive Rats: Dependence on Receptor Subtype, Salt Diet, and Sex.Hypertension. 2018 Aug;72(2):511-521. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.10765. Epub 2018 Jun 25. Hypertension. 2018. PMID: 29941515 Free PMC article.
-
Interactive roles of CD73 and tissue nonspecific alkaline phosphatase in the renal vascular metabolism of 5'-AMP.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014 Sep 15;307(6):F680-5. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00312.2014. Epub 2014 Jul 2. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24990899 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the N6-etheno-bridge method to assess extracellular metabolism of adenine nucleotides: detection of a possible role for purine nucleoside phosphorylase in adenosine metabolism.Purinergic Signal. 2020 Jun;16(2):187-211. doi: 10.1007/s11302-020-09699-x. Epub 2020 May 4. Purinergic Signal. 2020. PMID: 32367441 Free PMC article.
-
Role of CD73 in Renal Sympathetic Neurotransmission in the Mouse Kidney.Physiol Rep. 2013 Aug 20;1(3):e00057. doi: 10.1002/phy2.57. Physiol Rep. 2013. PMID: 24066228 Free PMC article.
-
Alkaline Phosphatase Inhibitors Attenuate Renovascular Responses to Norepinephrine.Hypertension. 2017 Mar;69(3):484-493. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.116.08623. Epub 2017 Jan 30. Hypertension. 2017. PMID: 28137984 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cotter G, Dittrich HC, Weatherley BD, Bloomfield DM, O'Connor CM, Metra M, Massie BM. The PROTECT pilot study: a randomized, placebo-controlled, dose-finding study of the adenosine A1 receptor antagonist rolofylline in patients with acute heart failure and renal impairment. J Card Fail 14: 631– 640, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Dittrich HC, Gupta DK, Hack TC, Dowling T, Callahan J, Thomson S. The effect of KW-3902, an adenosine A1 receptor antagonist, on renal function and renal plasma flow in ambulatory patients with heart failure and renal impairment. J Card Fail 13: 609– 617, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Fredholm BB, Duner-Engstrom M, Fastbom J, Hu PS, van der Ploeg I. Role of G proteins, cyclic AMP, and ion channels in the inhibition of transmitter release by adenosine. Ann NY Acad Sci 604: 276– 288, 1990 - PubMed
-
- Givertz MM, Massie BM, Fields TK, Pearson LL, Dittrich HC. The effects of KW-3902, an adenosine A1-receptor antagonist, on diuresis and renal function in patients with acute decompensated heart failure and renal impairment or diuretic resistance. J Am Coll Cardiol 50: 1551– 1560, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

