Snf1-related kinase inhibits colon cancer cell proliferation through calcyclin-binding protein-dependent reduction of β-catenin
- PMID: 22874833
- PMCID: PMC3475258
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.12-212282
Snf1-related kinase inhibits colon cancer cell proliferation through calcyclin-binding protein-dependent reduction of β-catenin
Abstract
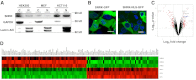
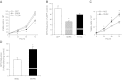
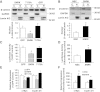
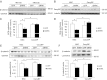
Sucrose nonfermenting 1 (Snf1)-related kinase (SNRK) is a serine/threonine kinase with sequence similarity to AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK); however, its function is not well characterized. We conducted a gene array to determine which genes are regulated by SNRK. The array demonstrated that SNRK overexpression increased the levels of genes involved in cell proliferation, including calcyclin-binding protein (CacyBP), a member of the ubiquitin ligase complex that targets nonphosphorylated β-catenin for degradation. We confirmed that SNRK increased CacyBP mRNA and protein, and decreased β-catenin protein in HCT116 and RKO colon cancer cells. Furthermore, SNRK inhibited colon cancer cell proliferation, and CacyBP down-regulation reversed the SNRK-mediated decrease in proliferation and β-catenin. SNRK overexpression also decreased β-catenin nuclear localization and target gene transcription, and β-catenin down-regulation reversed the effects of SNRK knockdown on proliferation. SNRK transcript levels were reduced in human colon tumors compared to normal tissue by 35.82%, and stable knockdown of SNRK increased colon cancer cell tumorigenicity. Our results demonstrate that SNRK is down-regulated in colon cancer and inhibits colon cancer cell proliferation through CacyBP up-regulation and β-catenin degradation, resulting in reduced proliferation signaling. These findings reveal a novel function for SNRK in the regulation of colon cancer cell proliferation and β-catenin signaling.
Figures

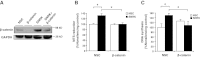

References
-
- Hardie D. G. (2007) AMP-activated/SNF1 protein kinases: conserved guardians of cellular energy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 8, 774–785 - PubMed
-
- Fogarty S., Hardie D. G. (2010) Development of protein kinase activators: AMPK as a target in metabolic disorders and cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1804, 581–591 - PubMed
-
- Bright N. J., Thornton C., Carling D. (2009) The regulation and function of mammalian AMPK-related kinases. Acta Physiol. (Oxf.) 196, 15–26 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

