Prevalence and significance of stroke symptoms among patients receiving maintenance dialysis
- PMID: 22875090
- PMCID: PMC3430712
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e31826845e9
Prevalence and significance of stroke symptoms among patients receiving maintenance dialysis
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this cross-sectional study was to determine the prevalence and potential significance of stroke symptoms among end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients without a prior diagnosis of stroke or TIA.
Methods: We enrolled 148 participants with ESRD from 5 clinics. Stroke symptoms and functional status, basic and instrumental activities of daily living (ADL, IADL), were ascertained by validated questionnaires. Cognitive function was assessed with a neurocognitive battery. Cognitive impairment was defined as a score 2 SDs below norms for age and education in 2 domains. IADL impairment was defined as needing assistance in at least 1 of 7 IADLs.
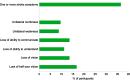
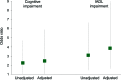
Results: Among the 126 participants without a prior stroke or TIA, 46 (36.5%) had experienced one or more stroke symptoms. After adjustment for age, sex, race, education, language, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease, participants with stroke symptoms had lower scores on tests of attention, psychomotor speed, and executive function, and more pronounced dependence in IADLs and ADLs (p ≤ 0.01 for all). After adjustment for age, sex, race, education, language, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease, participants with stroke symptoms had a higher likelihood of cognitive impairment (odds ratio [OR] 2.47, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.03-5.92) and IADL impairment (OR 3.86, 95% CI 1.60-9.28).
Conclusions: Stroke symptoms are common among patients with ESRD and strongly associated with impairments in cognition and functional status. These findings suggest that clinically significant stroke events may go undiagnosed in this high-risk population.
Figures
Comment in
-
Stroke symptoms signal worse outcomes in patients with end-stage renal disease.Neurology. 2012 Sep 4;79(10):960-1. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182684548. Epub 2012 Aug 8. Neurology. 2012. PMID: 22875084 No abstract available.
References
-
- Seliger SL, Gillen DL, Longstreth WT, Jr, Kestenbaum B, Stehman-Breen CO. Elevated risk of stroke among patients with end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int 2003; 64: 603– 609 . - PubMed
-
- Nakatani T, Naganuma T, Uchida J, et al. Silent cerebral infarction in hemodialysis patients. Am J Nephrol 2003; 23: 86– 90 . - PubMed
-
- Vermeer SE, Prins ND, den Heijer T, Hofman A, Koudstaal PJ, Breteler MM. Silent brain infarcts and the risk of dementia and cognitive decline. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 1215– 1222 . - PubMed
-
- Wadley VG, McClure LA, Howard VJ, et al. Cognitive status, stroke symptom reports, and modifiable risk factors among individuals with no diagnosis of stroke or transient ischemic attack in the Reasons for Geographic and Racial Differences in Stroke (REGARDS) study. Stroke 2007; 38: 1143– 1147 . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
