Alternative markers of hyperglycemia and risk of diabetes
- PMID: 22875225
- PMCID: PMC3476908
- DOI: 10.2337/dc12-0787
Alternative markers of hyperglycemia and risk of diabetes
Abstract
Objective: Fructosamine, glycated albumin, and 1,5-anhydroglucitol (1,5-AG) are of interest for monitoring short-term glycemic control in patients with diabetes; however, their associations with diabetes risk are uncharacterized.
Research design and methods: We used Cox proportional hazards models to examine the associations of fructosamine, glycated albumin, and 1,5-AG with incident diabetes in 1,299 participants, from the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study (2005-2006), who had no history of diagnosed diabetes at baseline. Incident diabetes was self-reported during annual telephone calls.
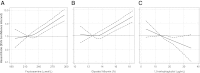
Results: There were 119 new cases of diabetes during a median follow-up of 3.3 years. When compared with the lowest quartile, the fourth quartiles of fructosamine and glycated albumin were significantly associated with diabetes risk (hazard ratio [HR] 3.99 [95% CI 1.93-8.28] and 5.22 [2.49-10.94], respectively). The fourth quartile of 1,5-AG was associated with a significantly lower diabetes risk (0.27 [0.14-0.55]). Associations were attenuated but still significant after adjustment for hemoglobin A(1c) (A1C) or fasting glucose.
Conclusions: Fructosamine, glycated albumin, and 1,5-AG were associated with the subsequent development of diabetes independently of baseline A1C and fasting glucose. Our results suggest these alternative biomarkers may be useful in identifying persons at risk for diabetes.
Figures
References
-
- Rondeau P, Bourdon E. The glycation of albumin: structural and functional impacts. Biochimie 2011;93:645–658 - PubMed
-
- Buse JB, Freeman JLR, Edelman SV, Jovanovic L, McGill JB. Serum 1,5-anhydroglucitol (GlycoMark): a short-term glycemic marker. Diabetes Technol Ther 2003;5:355–363 - PubMed
-
- Rubinow KB, Hirsch IB. Reexamining metrics for glucose control. JAMA 2011;305:1132–1133 - PubMed
-
- Freedman BI, Shenoy RN, Planer JA, et al. Comparison of glycated albumin and hemoglobin A1c concentrations in diabetic subjects on peritoneal and hemodialysis. Perit Dial Int 2010;30:72–79 - PubMed
-
- Peacock TP, Shihabi ZK, Bleyer AJ, et al. Comparison of glycated albumin and hemoglobin A(1c) levels in diabetic subjects on hemodialysis. Kidney Int 2008;73:1062–1068 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201100012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK089174/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007024/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK076595/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32HL007024/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005G/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK089174/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL075572/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL075572-01/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

