Korean clinical practice guidelines: otitis media in children
- PMID: 22876048
- PMCID: PMC3410229
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.8.835
Korean clinical practice guidelines: otitis media in children
Abstract
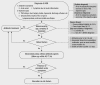
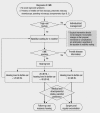
Acute otitis media (AOM) and otitis media with effusion (OME) are common infections in children, and their diagnosis and treatment have significant impacts on the health of children and the costs of providing national medical care. In 2009, the Korean Otologic Society organized a committee composed of experts in the field of otolaryngology, pediatrics, and family medicine to develop Korean clinical practice guidelines (CPG) for otitis media in children with the goal of meeting regional medical and social needs in Korea. For this purpose, the committee adapted existing guidelines. A comprehensive literature review was carried out primarily from 2004 to 2009 using medical search engines including data from Korea. A draft was written after a national questionnaire survey and several public audits, and it was editorially supervised by senior advisors before publication of the final report. These evidence-based guidelines for the management of otitis media in children provide recommendations to primary practitioners for the diagnosis and treatment of children younger than 15 yr old with uncomplicated AOM and OME. The guidelines include recommendations regarding diagnosis, treatment options, prevention and parent education, medical records, referral, and complementary/alternative medicine for treating pediatric otitis media.
Keywords: Acute Disease; Child; Diagnosis; Guideline; Otitis Media; Otitis Media with Effusion; Treatment.
Figures
References
-
- Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Korea health statistics 2009: Korea national health and nutrition examination survey (KNHANES IV-3) [accessed on 20 February 2012]. Available at http://www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/2004_report_update/e....
-
- Terris MH, Magit AE, Davidson TM. Otitis media with effusion in infants and children. Primary care concerns addressed from an otolaryngologist's perspective. Postgrad Med. 1995;97:137–138. 143–144, 147. - PubMed
-
- Kim JG, Sohn YT. Prevalence of otitis media with effusion in kindergarten children in Taegu area. Korean J Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 1995;38:1695–1703.
-
- Yeom MS, Lee SY, Lee HJ, Jeong KY. Prevalence of silent otitis media with effusion in preschool children in Kunsan city. J Korean Acad Fam Med. 1997;18:46–52.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical