Relationship between complex regional pain syndrome and working life: a Korean study
- PMID: 22876061
- PMCID: PMC3410242
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.8.929
Relationship between complex regional pain syndrome and working life: a Korean study
Abstract
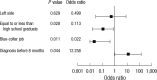
Complex regional pain syndrome affects the quality of life of the patient. The aim of this study was to investigate the epidemiological features of this syndrome and evaluate its effect on the patient's working life. We demonstrated that the disease has a male preponderance and is 3 times more likely to affect the lower extremities. In this study, 11 participants (20%) retained their employment, whereas 44 (80%) became unemployed. Mean age and pain score were lower in the employment group than in the unemployment group (29.1 ± 16.8 yr vs 40.1 ± 12.6 yr, P = 0.021, and 4.5 ± 2.9 vs 7.0 ± 2.0, P = 0.002, respectively). Subjects diagnosed within 8 months (P = 0.044), those who had achieved higher levels of education (P = 0.028), and those working in white-collar jobs (P = 0.011) had higher employment-retention rates. Therefore, patients must manage their jobs (lower physical demand and decrease the number of working hours) if they are to improve their occupational life. To achieve satisfactory outcomes and a high employment-retention rate, clinicians must be aware of the importance of an early diagnosis (within 8 months), appropriate treatment, and a reduction in the patient's pain score.
Keywords: Complex Regional Pain Syndromes; Employment; Work.
Figures
References
-
- de Mos M, Sturkenboom MC, Huygen FJ. Current understandings on complex regional pain syndrome. Pain Pract. 2009;9:86–99. - PubMed
-
- Jänig W, Baron R. Complex regional pain syndrome: mystery explained? Lancet Neurol. 2003;2:687–697. - PubMed
-
- Sandroni P. Complex regional pain syndrome type I: incidence and prevalence in Olmsted county, a population-based study. Pain. 2003;103:199–207. - PubMed
-
- de Mos M, Debruijn A, Huygen F, Dieleman J, Stricker B, Sturkenboom M. The incidence of complex regional pain syndrome: a population-based study. Pain. 2007;129:12–20. - PubMed
-
- Galer BS, Henderson J, Perander J, Jensen MP. Course of symptoms and quality of life measurement in complex regional pain syndrome: a pilot survey. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2000;20:286–292. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

