MicroRNA-196a promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and invasion through targeting HOXA5
- PMID: 22876840
- PMCID: PMC3503718
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-348
MicroRNA-196a promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and invasion through targeting HOXA5
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are short, non-coding RNAs (~22 nt) that play important roles in the pathogenesis of human diseases by negatively regulating gene expression. Although miR-196a has been implicated in several other cancers, its role in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is unknown. The aim of the present study was to examine the expression pattern of miR-196a in NSCLC and its clinical significance, as well as its biological role in tumor progression.
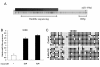
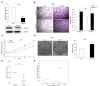
Methods: Expression of miR-196a was analyzed in 34 NSCLC tissues and five NSCLC cell lines by quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). The effect of DNA methylation on miR-196a expression was investigated by 5-aza-2-deoxy-cytidine treatment and bisulfite sequencing. The effect of miR-196a on proliferation was evaluated by MTT and colony formation assays, and cell migration and invasion were evaluated by transwell assays. Analysis of target protein expression was determined by western blotting. Luciferase reporter plasmids were constructed to confirm the action of miR-196a on downstream target genes, including HOXA5. Differences between the results were tested for significance using Student's t-test (two-tailed).
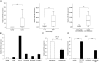
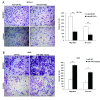
Results: miR-196a was highly expressed both in NSCLC samples and cell lines compared with their corresponding normal counterparts, and the expression of miR-196a may be affected by DNA demethylation. Higher expression of miR-196a in NSCLC tissues was associated with a higher clinical stage, and also correlated with NSCLC lymph-node metastasis. In vitro functional assays demonstrated that modulation of miR-196a expression affected NSCLC cell proliferation, migration and invasion. Our analysis showed that miR-196a suppressed the expression of HOXA5 both at the mRNA and protein levels, and luciferase assays confirmed that miR-196a directly bound to the 3'untranslated region of HOXA5. Knockdown of HOXA5 expression in A549 cells using RNAi was shown to promote NSCLC cell proliferation, migration and invasion. Finally, we observed an inverse correlation between HOXA5 and miR-196a expression in NSCLC tissues.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that miR-196a is significantly up-regulated in NSCLC tissues, and regulates NSCLC cell proliferation, migration and invasion, partially via the down-regulation of HOXA5. Thus, miR-196a may represent a potential therapeutic target for NSCLC intervention.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

