Development of an in vitro drug screening assay using Schistosoma haematobium schistosomula
- PMID: 22876861
- PMCID: PMC3437206
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-3305-5-165
Development of an in vitro drug screening assay using Schistosoma haematobium schistosomula
Abstract
Background: The development of novel antischistosomal drugs is crucial, as currently no vaccine and only a single drug is available for the treatment of schistosomiasis. Fast and accurate in vitro assays are urgently needed to identify new drug candidates and research efforts should include Schistosoma haematobium. The aim of the present study was to develop a S. haematobium drug sensitivity assay based on newly transformed schistosomula (NTS).
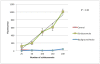
Methods: We first undertook comparative studies on the cercarial emergence rhythms of the intermediate host snails Biomphalaria glabrata (S. mansoni) and Bulinus truncatus (S. haematobium). Two transformation methods as well as three purification methods were studied on S. haematobium cercariae in order to produce a large number of viable and clean NTS. Known antischistosomal drugs were tested in the established NTS assay in vitro. Drug effects were evaluated either microscopically or fluorometrically, using a resazurin based viability marker. Microscopically obtained IC₅₀ values were compared with results obtained for S. mansoni.
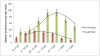
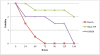
Results: A circadian rhythm existed in both snail species. Infected B. truncatus snails shed less cercariae than B. glabrata during the testing period. The highest transformation rate (69%) of S. haematobium cercariae into NTS was obtained with the vortex transformation (mechanical input) and the highest purification factor was observed using Percoll®. The fluorimetric readout based on resazurin was very precise in detecting dead or/and severely damaged schistosomula.
Conclusions: With the use of viability markers such as resazurin, drug screening assays using S. haematobium NTS can be efficiently performed. However, drugs acting on the morphology and motility of S. haematobium NTS, such as metrifonate are missed. Drug sensitivity assays with NTS of both species, S. haematobium and S. mansoni, showed very similar results using known antischistosomal drugs. The S. mansoni NTS assay might be more suitable as primary screen in drug discovery efforts, which ultimately aim for a broad-spectrum antischistosomal drug as a larger number of S. mansoni NTS can be generated.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fluorescence/luminescence-based markers for the assessment of Schistosoma mansoni schistosomula drug assays.Parasit Vectors. 2015 Dec 8;8:624. doi: 10.1186/s13071-015-1233-3. Parasit Vectors. 2015. PMID: 26644133 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of praziquantel and reinfection patterns in single and mixed infection foci for intestinal and urogenital schistosomiasis in Cameroon.Acta Trop. 2013 Nov;128(2):275-83. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2013.06.007. Epub 2013 Jun 20. Acta Trop. 2013. PMID: 23791803
-
Molecular characterization and distribution of Schistosoma cercariae collected from naturally infected bulinid snails in northern and central Côte d'Ivoire.Parasit Vectors. 2019 Mar 19;12(1):117. doi: 10.1186/s13071-019-3381-3. Parasit Vectors. 2019. PMID: 30890180 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between intermediate snail hosts of the genus Bulinus and schistosomes of the Schistosoma haematobium group.Parasitology. 2001;123 Suppl:S245-60. doi: 10.1017/s0031182001008046. Parasitology. 2001. PMID: 11769287 Review.
-
Mechanically produced schistosomula as a higher-throughput tools for phenotypic pre-screening in drug sensitivity assays: current research and future trends.Biomark Res. 2016 Nov 22;4:21. doi: 10.1186/s40364-016-0075-2. eCollection 2016. Biomark Res. 2016. PMID: 27895916 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Current drug targets for helminthic diseases.Parasitol Res. 2013 May;112(5):1819-31. doi: 10.1007/s00436-013-3383-6. Epub 2013 Mar 26. Parasitol Res. 2013. PMID: 23529336 Review.
-
The computationally predicted drug-likeness, pharmacokinetics properties, medicinal chemistry parameters, and toxicity properties of Cucurbita maxima compounds.F1000Res. 2022 Oct 31;11:Chem Inf Sci-1234. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.127126.1. eCollection 2022. F1000Res. 2022. PMID: 38690404 Free PMC article.
-
Use of kinase inhibitors against schistosomes to improve and broaden praziquantel efficacy.Parasitology. 2020 Nov;147(13):1488-1498. doi: 10.1017/S0031182020001250. Epub 2020 Aug 3. Parasitology. 2020. PMID: 32741402 Free PMC article.
-
The antioxidants resveratrol and N-acetylcysteine enhance anthelmintic activity of praziquantel and artesunate against Schistosoma mansoni.Parasit Vectors. 2019 Jun 20;12(1):309. doi: 10.1186/s13071-019-3566-9. Parasit Vectors. 2019. PMID: 31221193 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of clinically approved HDAC inhibitors on Plasmodium, Leishmania and Schistosoma parasite growth.Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2017 Apr;7(1):42-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2016.12.005. Epub 2016 Dec 23. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2017. PMID: 28107750 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Manson-Bahr PEC, Bell DR. Manson’s Tropical Diseases. Bailliere Tindall. 22. , ; 2008.
-
- The World Health Report 2003: shaping the future. World Health Organization, Geneva; 2003.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

