Molecular epidemiology and clinical manifestations of human cryptosporidiosis in Sweden
- PMID: 22877562
- PMCID: PMC9151846
- DOI: 10.1017/S0950268812001665
Molecular epidemiology and clinical manifestations of human cryptosporidiosis in Sweden
Abstract
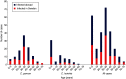
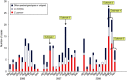
This study describes the epidemiology and symptoms in 271 cryptosporidiosis patients in Stockholm County, Sweden. Species/genotypes were determined by polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment-length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) of the Cryptosporidium oocyst wall protein (COWP) and 18S rRNA genes. Species were C. parvum (n=111), C. hominis (n=65), C. meleagridis (n=11), C. felis (n=2), Cryptosporidium chipmunk genotype 1 (n=2), and a recently described species, C. viatorum (n=2). Analysis of the Gp60 gene revealed five C. hominis allele families (Ia, Ib, Id, Ie, If), and four C. parvum allele families (IIa, IIc, IId, IIe). Most C. parvum cases (51%) were infected in Sweden, as opposed to C. hominis cases (26%). Clinical manifestations differed slightly by species. Diarrhoea lasted longer in C. parvum cases compared to C. hominis and C. meleagridis cases. At follow-up 25-36 months after disease onset, 15% of the patients still reported intermittent diarrhoea. In four outbreaks and 13 family clusters, a single subtype was identified, indicating a common infection source, which emphasizes the value of genotyping for epidemiological investigations.
Figures
References
-
- Fayer R. General biology. In Fayer R, Xiao L, eds. Cryptosporidium and Cryptosporidiosis, 2nd edn. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2008, pp. 1–42.
-
- Fayer R, Santin M, Macarisin D. Cryptosporidium ubiquitum n.sp. in animals and humans. Veterinary Parasitology 2011; 172: 23–32. - PubMed
-
- Fayer R, Santin M. Cryptosporidium xiaoi n.sp. (Apicomplexa: Cryptosporidiidae) in sheep (Ovis aries). Veterinary Parasitology 2009; 164: 192–200. - PubMed
-
- Plutzer J, Karanis P. Genetic polymorphism in Cryptosporidium species: an update. Veterinary Parasitology 2009; 165: 187–199. - PubMed

