Cell biology of ischemia/reperfusion injury
- PMID: 22878108
- PMCID: PMC3904795
- DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394309-5.00006-7
Cell biology of ischemia/reperfusion injury
Abstract
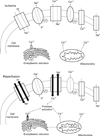
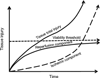
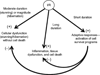
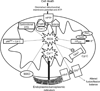
Disorders characterized by ischemia/reperfusion (I/R), such as myocardial infarction, stroke, and peripheral vascular disease, continue to be among the most frequent causes of debilitating disease and death. Tissue injury and/or death occur as a result of the initial ischemic insult, which is determined primarily by the magnitude and duration of the interruption in the blood supply, and then subsequent damage induced by reperfusion. During prolonged ischemia, ATP levels and intracellular pH decrease as a result of anaerobic metabolism and lactate accumulation. As a consequence, ATPase-dependent ion transport mechanisms become dysfunctional, contributing to increased intracellular and mitochondrial calcium levels (calcium overload), cell swelling and rupture, and cell death by necrotic, necroptotic, apoptotic, and autophagic mechanisms. Although oxygen levels are restored upon reperfusion, a surge in the generation of reactive oxygen species occurs and proinflammatory neutrophils infiltrate ischemic tissues to exacerbate ischemic injury. The pathologic events induced by I/R orchestrate the opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore, which appears to represent a common end-effector of the pathologic events initiated by I/R. The aim of this treatise is to provide a comprehensive review of the mechanisms underlying the development of I/R injury, from which it should be apparent that a combination of molecular and cellular approaches targeting multiple pathologic processes to limit the extent of I/R injury must be adopted to enhance resistance to cell death and increase regenerative capacity in order to effect long-lasting repair of ischemic tissues.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Adibhatha RM, Hatcher JF. Lipid oxidation and peroxidation in CNS health and disease: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2010;12:125–169. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

