The evaluation of hepatitis C virus core antigen in immunized BALB/c mice
- PMID: 22879829
- PMCID: PMC3412556
- DOI: 10.5812/hepatmon.6141
The evaluation of hepatitis C virus core antigen in immunized BALB/c mice
Abstract
Background: Hepatitis infection represents one of the important causes of morbidity and mortality in developing countries, however there is not any effective vaccine against hepatitis C which is one of the significant problems in vaccine project.
Objectives: The aim of the present study is to evaluate the role of HCV core protein in inducing IFN-Gamma secretion and TCL activities as a vaccine in Balb/C mice.
Material and methods: Our previous cloned plasmid (HCV Core gene into pETDuet-1) applied for protein expression in bacteria. The expressed and purified recombinant protein together with Freund's adjuvant was injected to 15 Balb/c mice. The total IgG and IgG2a of immunized mice sera were evaluated after a week. Two weeks after booster injection, we studied the proliferation and IFNγ secretion of spleens, inguinal and popliteal lymph nodes lymphocytes by ELISA and ELISPOT.
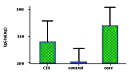
Results: The FSFC (Frequency of spot forming cells) of secreting cells of immunized mice with HCV/Core protein and sera IgG2a were considerably higher than the control groups.
Conclusions: The core protein together with proper adjuvant can be a candidate vaccine against of HCV infection.
Keywords: Core protein; Hepacivirus; Recombinant Proteins.
Figures




References
-
- Li D, Takyar ST, Lott WB, Gowans EJ. Amino acids 1-20 of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) core protein specifically inhibit HCV IRES-dependent translation in HepG2 cells, and inhibit both HCV IRESand cap-dependent translation in HuH7 and CV-1 cells. J Gen Virol. 2003;84(Pt 4):815–25. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.18697-0. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
