Osteopontin reduces biofilm formation in a multi-species model of dental biofilm
- PMID: 22879891
- PMCID: PMC3413689
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041534
Osteopontin reduces biofilm formation in a multi-species model of dental biofilm
Abstract
Background: Combating dental biofilm formation is the most effective means for the prevention of caries, one of the most widespread human diseases. Among the chemical supplements to mechanical tooth cleaning procedures, non-bactericidal adjuncts that target the mechanisms of bacterial biofilm formation have gained increasing interest in recent years. Milk proteins, such as lactoferrin, have been shown to interfere with bacterial colonization of saliva-coated surfaces. We here study the effect of bovine milk osteopontin (OPN), a highly phosphorylated whey glycoprotein, on a multispecies in vitro model of dental biofilm. While considerable research effort focuses on the interaction of OPN with mammalian cells, there are no data investigating the influence of OPN on bacterial biofilms.
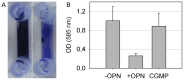
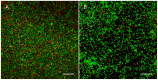
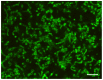
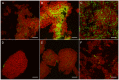
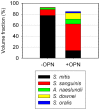
Methodology/principal findings: Biofilms consisting of Streptococcus oralis, Actinomyces naeslundii, Streptococcus mitis, Streptococcus downei and Streptococcus sanguinis were grown in a flow cell system that permitted in situ microscopic analysis. Crystal violet staining showed significantly less biofilm formation in the presence of OPN, as compared to biofilms grown without OPN or biofilms grown in the presence of caseinoglycomacropeptide, another phosphorylated milk protein. Confocal microscopy revealed that OPN bound to the surface of bacterial cells and reduced mechanical stability of the biofilms without affecting cell viability. The bacterial composition of the biofilms, determined by fluorescence in situ hybridization, changed considerably in the presence of OPN. In particular, colonization of S. mitis, the best biofilm former in the model, was reduced dramatically.
Conclusions/significance: OPN strongly reduces the amount of biofilm formed in a well-defined laboratory model of acidogenic dental biofilm. If a similar effect can be observed in vivo, OPN might serve as a valuable adjunct to mechanical tooth cleaning procedures.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of osteopontin on the initial adhesion of dental bacteria.J Nat Prod. 2012 Dec 28;75(12):2108-12. doi: 10.1021/np300514z. Epub 2012 Nov 20. J Nat Prod. 2012. PMID: 23167781
-
Calcium-Phosphate-Osteopontin Particles Reduce Biofilm Formation and pH Drops in in situ Grown Dental Biofilms.Caries Res. 2017;51(1):26-33. doi: 10.1159/000451064. Epub 2016 Dec 14. Caries Res. 2017. PMID: 27960182
-
pH landscapes in a novel five-species model of early dental biofilm.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e25299. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025299. Epub 2011 Sep 23. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21966490 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive strategies for overcoming dental biofilms: Microbial dynamics and innovative methods.Microb Pathog. 2025 Aug;205:107690. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2025.107690. Epub 2025 May 9. Microb Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40349996 Review.
-
Current understanding of multi-species biofilms.Int J Oral Sci. 2011 Apr;3(2):74-81. doi: 10.4248/IJOS11027. Int J Oral Sci. 2011. PMID: 21485311 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of canonical NF-κB signaling pathway on the proliferation and odonto/osteogenic differentiation of human stem cells from apical papilla.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:319651. doi: 10.1155/2014/319651. Epub 2014 Apr 23. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24864235 Free PMC article.
-
GATA4 regulates osteoblastic differentiation and bone remodeling via p38-mediated signaling.J Mol Histol. 2017 Jun;48(3):187-197. doi: 10.1007/s10735-017-9719-2. Epub 2017 Apr 9. J Mol Histol. 2017. PMID: 28393293
-
Osteopontin adsorption to Gram-positive cells reduces adhesion forces and attachment to surfaces under flow.J Oral Microbiol. 2017 Oct 11;9(1):1379826. doi: 10.1080/20002297.2017.1379826. eCollection 2017. J Oral Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29081915 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental and Theoretical Investigation of Multispecies Oral Biofilm Resistance to Chlorhexidine Treatment.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 21;6:27537. doi: 10.1038/srep27537. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27325010 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention of Initial Bacterial Attachment by Osteopontin and Other Bioactive Milk Proteins.Biomedicines. 2022 Aug 9;10(8):1922. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10081922. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36009469 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ong G (1990) The effectiveness of 3 types of dental floss for interdental plaque removal. J Clin Periodontol 17: 463–466. - PubMed
-
- van der Weijden GA, Hioe KP (2005) A systematic review of the effectiveness of self-performed mechanical plaque removal in adults with gingivitis using a manual toothbrush. J Clin Periodontol 32 Suppl 6214–228. - PubMed
-
- Prasad KV, Sreenivasan PK, Patil S, Chhabra KG, Javali SB, et al. (2011) Removal of dental plaque from different regions of the mouth after a 1-minute episode of mechanical oral hygiene. Am J Dent 24: 60–64. - PubMed
-
- Petersen PE (2003) The World Oral Health Report 2003: continuous improvement of oral health in the 21st century – the approach of the WHO Global Oral Health Programme. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol 31 Suppl 13–23. - PubMed
-
- Gaffar A, Afflitto J, Nabi N (1997) Chemical agents for the control of plaque and plaque microflora: an overview. Eur J Oral Sci 105: 502–507. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

