Binding of the heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein K (hnRNP K) to the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 (EBNA2) enhances viral LMP2A expression
- PMID: 22879910
- PMCID: PMC3411732
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042106
Binding of the heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein K (hnRNP K) to the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 (EBNA2) enhances viral LMP2A expression
Abstract
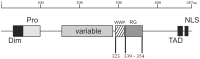
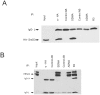
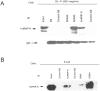
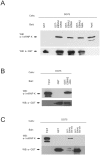
The Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) -encoded EBNA2 protein, which is essential for the in vitro transformation of B-lymphocytes, interferes with cellular processes by binding to proteins via conserved sequence motifs. Its Arginine-Glycine (RG) repeat element contains either symmetrically or asymmetrically di-methylated arginine residues (SDMA and ADMA, respectively). EBNA2 binds via its SDMA-modified RG-repeat to the survival motor neurons protein (SMN) and via the ADMA-RG-repeat to the NP9 protein of the human endogenous retrovirus K (HERV-K (HML-2) Type 1). The hypothesis of this work was that the methylated RG-repeat mimics an epitope shared with cellular proteins that is used for interaction with target structures. With monoclonal antibodies against the modified RG-repeat, we indeed identified cellular homologues that apparently have the same surface structure as methylated EBNA2. With the SDMA-specific antibodies, we precipitated the Sm protein D3 (SmD3) which, like EBNA2, binds via its SDMA-modified RG-repeat to SMN. With the ADMA-specific antibodies, we precipitated the heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein K (hnRNP K). Specific binding of the ADMA- antibody to hnRNP K was demonstrated using E. coli expressed/ADMA-methylated hnRNP K. In addition, we show that EBNA2 and hnRNP K form a complex in EBV- infected B-cells. Finally, hnRNP K, when co-expressed with EBNA2, strongly enhances viral latent membrane protein 2A (LMP2A) expression by an unknown mechanism as we did not detect a direct association of hnRNP K with DNA-bound EBNA2 in gel shift experiments. Our data support the notion that the methylated surface of EBNA2 mimics the surface structure of cellular proteins to interfere with or co-opt their functional properties.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Kieff E, Rickinson AE (2007) Epstein-Barr Virus and its replication. In: Knipe D, Griffin DE, Lamb RA, Strauss SE, Howley PM, et al., editors. editors. Fields Virology. 5 ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven. 2603–2654.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

