c-Abl is an upstream regulator of acid sphingomyelinase in apoptosis induced by inhibition of integrins αvβ3 and αvβ5
- PMID: 22879933
- PMCID: PMC3411766
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042291
c-Abl is an upstream regulator of acid sphingomyelinase in apoptosis induced by inhibition of integrins αvβ3 and αvβ5
Abstract
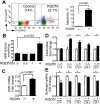
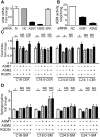
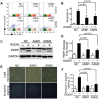
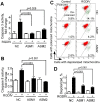
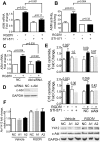
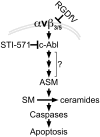
Inhibition of integrins αvβ3/αvβ5 by the cyclic function-blocking peptide, RGDfV (Arg-Gly-Asp-Phe-Val) can induce apoptosis in both normal cells and tumor cells. We show that RGDfV induced apoptosis in ECV-304 carcinoma cells, increased activity and mRNA expression of acid sphingomyelinase (ASM), and increased ceramides C(16), C(18:0), C(24:0) and C(24:1) while decreasing the corresponding sphingomyelins. siRNA to ASM decreased RGDfV-induced apoptosis as measured by TUNEL, PARP cleavage, mitochondrial depolarization, and caspase-3 and caspase-8 activities, as well as by annexinV in a 3D collagen model. These findings indicate a causal role for ASM in RGDfV-induced apoptosis in ECV-304. We have shown that c-Abl, a non-receptor tyrosine kinase, also mediates RGDfV-induced apoptosis. However, c-Abl, has not been previously linked to ASM in any system. Here we show that STI-571 (imatinib, inhibitor of c-Abl) inhibited RGDfV-induced ASM activity. Furthermore, STI-571 and c-Abl-siRNA both inhibited RGDfV-induced increase in ASM mRNA, but ASM-siRNA did not affect c-Abl phosphorylation or expression, supporting that c-Abl regulates the RGDfV-induced increase in ASM expression. These studies implicate ASM as a mediator of apoptosis induced by inhibition of integrins αvβ3/αvβ5, and for the first time place c-Abl as an upstream regulator of ASM expression and activity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

