Increased cardiovascular and renal risk is associated with low nephron endowment in aged females: an ovine model of fetal unilateral nephrectomy
- PMID: 22879965
- PMCID: PMC3411741
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042400
Increased cardiovascular and renal risk is associated with low nephron endowment in aged females: an ovine model of fetal unilateral nephrectomy
Abstract
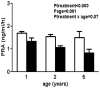
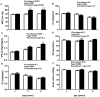
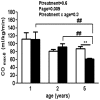
Previously we have shown that ovariectomised (OVX) female sheep have reduced renal function and elevated blood pressure from 6 months of age following fetal uninephrectomy (uni-x) at 100 days of gestation (term = 150 days). In the current study we examined if in intact female sheep the onset of decline in renal function and elevation in blood pressure was prevented. Studies were performed at 1 year, 2 and 5 years of age. Following fetal uni-x at 100 days, intact female sheep had ~30% reduction in glomerular filtration rate (GFR) at 1 year, which did not exacerbate with age (P(treatment) = 0.0001, P(age) = 0.7). In contrast renal blood flow was similar between the treatment groups at 1 year of age but had declined in the uni-x animals at 5 years of age (P(treatment × age) = 0.046). Interestingly, intact uni-x sheep did not develop elevations in arterial pressure until 2 years of age. Furthermore, uni-x animals had a similar capacity to respond to a cardiac challenge at 1 year and 2 years of age, however, cardiac functional reserve was significantly reduced compared to sham group at 5 years of age. Uni-x animals exhibited an increase in left ventricular dimensions at 5 years of age compared to the sham animals and compared to 2 years of age (P(treatment)<0.001, P(treatment × age)<0.001). In conclusion, the onset of renal dysfunction preceded the onset of hypertension in intact female uni-x sheep. Furthermore, this study showed that the intact females are protected from the impact of a reduced nephron endowment on cardiovascular health early in life as opposed to our findings in young male sheep and OVX uni-x female sheep. However, with ageing this protection is lost as evidenced by presence of left ventricular hypertrophy and impaired cardiac function in 5 year old uni-x female sheep.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Silbiger SR (2011) Raging hormones: gender and renal disease. Kidney Int 79: 382–384. - PubMed
-
- Reckelhoff JF (2008) Sex and sex steroids in cardiovascular-renal physiology and pathophysiology. Gend Med 5 Suppl A. S1–2. - PubMed
-
- Brenner BM, Mackenzie HS (1997) Nephron mass as a risk factor for progression of renal disease. Kidney Int. Suppl 63S124–127. - PubMed
-
- Woods LL, Ingelfinger JR, Nyengaard JR, Rasch R (2001) Maternal Protein Restriction Suppresses the Newborn Renin-Angiotensin System and Programs Adult Hypertension in Rats. Pediatr Res 49: 460–467. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

