Production of a subunit vaccine candidate against porcine post-weaning diarrhea in high-biomass transplastomic tobacco
- PMID: 22879967
- PMCID: PMC3411772
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042405
Production of a subunit vaccine candidate against porcine post-weaning diarrhea in high-biomass transplastomic tobacco
Abstract
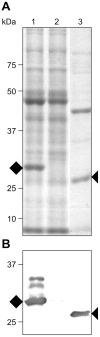
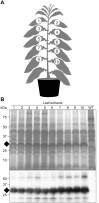
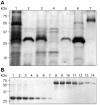
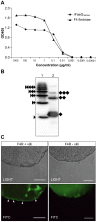
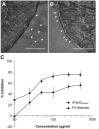
Post-weaning diarrhea (PWD) in piglets is a major problem in piggeries worldwide and results in severe economic losses. Infection with Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) is the key culprit for the PWD disease. F4 fimbriae of ETEC are highly stable proteinaceous polymers, mainly composed of the major structural subunit FaeG, with a capacity to evoke mucosal immune responses, thus demonstrating a potential to act as an oral vaccine against ETEC-induced porcine PWD. In this study we used a transplastomic approach in tobacco to produce a recombinant variant of the FaeG protein, rFaeG(ntd/dsc), engineered for expression as a stable monomer by N-terminal deletion and donor strand-complementation (ntd/dsc). The generated transplastomic tobacco plants accumulated up to 2.0 g rFaeG(ntd/dsc) per 1 kg fresh leaf tissue (more than 1% of dry leaf tissue) and showed normal phenotype indistinguishable from wild type untransformed plants. We determined that chloroplast-produced rFaeG(ntd/dsc) protein retained the key properties of an oral vaccine, i.e. binding to porcine intestinal F4 receptors (F4R), and inhibition of the F4-possessing (F4+) ETEC attachment to F4R. Additionally, the plant biomass matrix was shown to delay degradation of the chloroplast-produced rFaeG(ntd/dsc) in gastrointestinal conditions, demonstrating a potential to function as a shelter-vehicle for vaccine delivery. These results suggest that transplastomic plants expressing the rFaeG(ntd/dsc) protein could be used for production and, possibly, delivery of an oral vaccine against porcine F4+ ETEC infections. Our findings therefore present a feasible approach for developing an oral vaccination strategy against porcine PWD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Fairbrother JM, Nadeau E, Gyles CL (2005) Escherichia coli in postweaning diarrhea in pigs: an update on bacterial types, pathogenesis, and prevention strategies. Anim Health Res Rev 6: 17–39. - PubMed
-
- Hampson DJ (1994) Postweaning Escherichia coli diarrhoea in pigs. In: Gyles CL, editor. Escherichia coli in domestic animals and humans. Wallingford: CAB International. 171–191.
-
- Bertschinger HU, Fairbrother JM (1999) Escherichia coli infections. In: Straw BE, D’Allaire S, Mengeling WL, Taylor DJ, editors. Diseases of Swine, 8th Edition. Iowa: Iowa State University Press. 431–454.
-
- Ciosek D, Truszczynski M, Jagodzinski M (1983) The effectiveness of inactivated vaccines applied parenterally to sows to control Escherichia coli diarrhea in piglets in an industrial fattening farm. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 6: 313–319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

