Functional and molecular characterization of the role of CTCF in human embryonic stem cell biology
- PMID: 22879976
- PMCID: PMC3411781
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042424
Functional and molecular characterization of the role of CTCF in human embryonic stem cell biology
Abstract
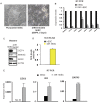
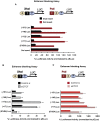
The CCCTC-binding factor CTCF is the only known vertebrate insulator protein and has been shown to regulate important developmental processes such as imprinting, X-chromosome inactivation and genomic architecture. In this study, we examined the role of CTCF in human embryonic stem cell (hESC) biology. We demonstrate that CTCF associates with several important pluripotency genes, including NANOG, SOX2, cMYC and LIN28 and is critical for hESC proliferation. CTCF depletion impacts expression of pluripotency genes and accelerates loss of pluripotency upon BMP4 induced differentiation, but does not result in spontaneous differentiation. We find that CTCF associates with the distal ends and internal sites of the co-regulated 160 kb NANOG-DPPA3-GDF3 locus. Each of these sites can function as a CTCF-dependent enhancer-blocking insulator in heterologous assays. In hESCs, CTCF exists in multisubunit protein complexes and can be poly(ADP)ribosylated. Known CTCF cofactors, such as Cohesin, differentially co-localize in the vicinity of specific CTCF binding sites within the NANOG locus. Importantly, the association of some cofactors and protein PARlation selectively changes upon differentiation although CTCF binding remains constant. Understanding how unique cofactors may impart specialized functions to CTCF at specific genomic locations will further illuminate its role in stem cell biology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Orkin SH, Wang J, Kim J, Chu J, Rao S, et al. (2008) The transcriptional network controlling pluripotency in ES cells. Cold Spring Harbor symposia on quantitative biology 73: 195–202. - PubMed
-
- Chia NY, Chan YS, Feng B, Lu X, Orlov YL, et al. (2010) A genome-wide RNAi screen reveals determinants of human embryonic stem cell identity. Nature 468: 316–320. - PubMed
-
- Tutter AV, Kowalski MP, Baltus GA, Iourgenko V, Labow M, et al. (2009) Role for Med12 in regulation of Nanog and Nanog target genes. J Biol Chem 284: 3709–3718. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

