The expression of tubulin cofactor A (TBCA) is regulated by a noncoding antisense Tbca RNA during testis maturation
- PMID: 22880023
- PMCID: PMC3412815
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042536
The expression of tubulin cofactor A (TBCA) is regulated by a noncoding antisense Tbca RNA during testis maturation
Abstract
Background: Recently, long noncoding RNAs have emerged as pivotal molecules for the regulation of coding genes' expression. These molecules might result from antisense transcription of functional genes originating natural antisense transcripts (NATs) or from transcriptional active pseudogenes. TBCA interacts with β-tubulin and is involved in the folding and dimerization of new tubulin heterodimers, the building blocks of microtubules.
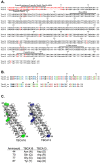
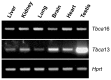
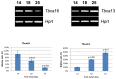
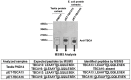
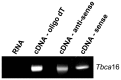
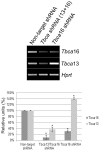
Methodology/principal findings: We found that the mouse genome contains two structurally distinct Tbca genes located in chromosomes 13 (Tbca13) and 16 (Tbca16). Interestingly, the two Tbca genes albeit ubiquitously expressed, present differential expression during mouse testis maturation. In fact, as testis maturation progresses Tbca13 mRNA levels increase progressively, while Tbca16 mRNA levels decrease. This suggests a regulatory mechanism between the two genes and prompted us to investigate the presence of the two proteins. However, using tandem mass spectrometry we were unable to identify the TBCA16 protein in testis extracts even in those corresponding to the maturation step with the highest levels of Tbca16 transcripts. These puzzling results led us to re-analyze the expression of Tbca16. We then detected that Tbca16 transcription produces sense and natural antisense transcripts. Strikingly, the specific depletion by RNAi of these transcripts leads to an increase of Tbca13 transcript levels in a mouse spermatocyte cell line.
Conclusions/significance: Our results demonstrate that Tbca13 mRNA levels are post-transcriptionally regulated by the sense and natural antisense Tbca16 mRNA levels. We propose that this regulatory mechanism operates during spermatogenesis, a process that involves microtubule rearrangements, the assembly of specific microtubule structures and requires critical TBCA levels.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Naturally occurring testis-specific histone H3 antisense transcripts in Drosophila.Mol Reprod Dev. 1997 Dec;48(4):413-20. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-2795(199712)48:4<413::AID-MRD1>3.0.CO;2-T. Mol Reprod Dev. 1997. PMID: 9364435
-
The complexity of antisense transcription revealed by the study of developing male germ cells.Genomics. 2006 Jun;87(6):681-92. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2005.12.006. Epub 2006 Feb 3. Genomics. 2006. PMID: 16458478
-
[Natural antisense transcript and its mechanism of gene regulation].Yi Chuan. 2010 Feb;32(2):122-8. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1005.2010.00122. Yi Chuan. 2010. PMID: 20176555 Review. Chinese.
-
Noncoding transcripts in sense and antisense orientation regulate the epigenetic state of ribosomal RNA genes.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2010;75:357-64. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2010.75.060. Epub 2011 Apr 18. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2010. PMID: 21502405
-
Natural antisense and noncoding RNA transcripts as potential drug targets.Drug Discov Today. 2006 Jun;11(11-12):503-8. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2006.04.013. Drug Discov Today. 2006. PMID: 16713901 Review.
Cited by
-
Downregulation of ZEB2-AS1 decreased tumor growth and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Nov;14(5):4606-4612. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5836. Epub 2016 Oct 12. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27748842 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic transgenerational inheritance, gametogenesis and germline development†.Biol Reprod. 2021 Sep 14;105(3):570-592. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioab085. Biol Reprod. 2021. PMID: 33929020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The presence, role and clinical use of spermatozoal RNAs.Hum Reprod Update. 2013 Nov-Dec;19(6):604-24. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmt031. Epub 2013 Jul 14. Hum Reprod Update. 2013. PMID: 23856356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural antisense transcripts as therapeutic targets.Drug Discov Today Ther Strateg. 2013 Fall;10(3):e119-e125. doi: 10.1016/j.ddstr.2013.03.001. Drug Discov Today Ther Strateg. 2013. PMID: 25580147 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Non-coding RNA regulation in reproduction: Their potential use as biomarkers.Noncoding RNA Res. 2019 May 3;4(2):54-62. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2019.04.001. eCollection 2019 Jun. Noncoding RNA Res. 2019. PMID: 31193491 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mattick JS, Makunin IV (2006) Non-coding RNA. Hum Mol Genet 15: R17–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

