BRAFV600E negatively regulates the AKT pathway in melanoma cell lines
- PMID: 22880048
- PMCID: PMC3411810
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042598
BRAFV600E negatively regulates the AKT pathway in melanoma cell lines
Abstract
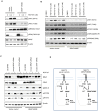
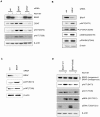
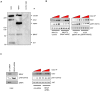
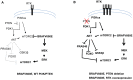
Cross-feedback activation of MAPK and AKT pathways is implicated as a resistance mechanism for cancer therapeutic agents targeting either RAF/MEK or PI3K/AKT/mTOR. It is thus important to have a better understanding of the molecular resistance mechanisms to improve patient survival benefit from these agents. Here we show that BRAFV600E is a negative regulator of the AKT pathway. Expression of BRAFV600E in NIH3T3 cells significantly suppresses MEK inhibitor (RG7167) or mTORC1 inhibitor (rapamycin) induced AKT phosphorylation (pAKT) and downstream signal activation. Treatment-induced pAKT elevation is found in BRAF wild type melanoma cells but not in a subset of melanoma cell lines harboring BRAFV600E. Knock-down of BRAFV600E in these melanoma cells elevates basal pAKT and downstream signals, whereas knock-down of CRAF, MEK1/2 or ERK1/2 or treatment with a BRAF inhibitor have no impact on pAKT. Mechanistically, we show that BRAFV600E interacts with rictor complex (mTORC2) and regulates pAKT through mTORC2. BRAFV600E is identified in mTORC2 after immunoprecipitation of rictor. Knock-down of rictor abrogates BRAFV600E depletion induced pAKT. Knock-down of BRAFV600E enhances cellular enzyme activity of mTORC2. Aberrant activation of AKT pathway by PTEN loss appears to override the negative impact of BRAFV600E on pAKT. Taken together, our findings suggest that in a subset of BRAFV600E melanoma cells, BRAFV600E negatively regulates AKT pathway in a rictor-dependent, MEK/ERK and BRAF kinase-independent manner. Our study reveals a novel molecular mechanism underlying the regulation of feedback loops between the MAPK and AKT pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Reversing melanoma cross-resistance to BRAF and MEK inhibitors by co-targeting the AKT/mTOR pathway.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28973. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028973. Epub 2011 Dec 14. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22194965 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of combined mTOR and MEK inhibition in uveal melanoma is driven by tumor genotype.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e40439. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040439. Epub 2012 Jul 10. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22808163 Free PMC article.
-
BRAFV600E cooperates with PI3K signaling, independent of AKT, to regulate melanoma cell proliferation.Mol Cancer Res. 2014 Mar;12(3):447-63. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-13-0224-T. Epub 2014 Jan 14. Mol Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24425783 Free PMC article.
-
MEK and RAF inhibitors for BRAF-mutated cancers.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2012 Oct 12;14:e17. doi: 10.1017/erm.2012.11. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 23058743 Review.
-
The role of the PI3K-AKT pathway in melanoma.Cancer J. 2012 Mar-Apr;18(2):142-7. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0b013e31824d448c. Cancer J. 2012. PMID: 22453015 Review.
Cited by
-
Phase I Study of the BRAF Inhibitor Vemurafenib in Combination With the Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Inhibitor Everolimus in Patients With BRAF-Mutated Malignancies.JCO Precis Oncol. 2018 Sep 13;2:PO.18.00189. doi: 10.1200/PO.18.00189. eCollection 2018. JCO Precis Oncol. 2018. PMID: 32913986 Free PMC article.
-
Akt inhibition enhances the cytotoxic effect of apigenin in combination with PLX4032 in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cells harboring BRAFV600E.J Endocrinol Invest. 2013 Dec;36(11):1099-104. doi: 10.3275/9099. Epub 2013 Sep 27. J Endocrinol Invest. 2013. PMID: 24084189
-
NAD/NAMPT and mTOR Pathways in Melanoma: Drivers of Drug Resistance and Prospective Therapeutic Targets.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 1;23(17):9985. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179985. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Expression of Key Guidance Genes at a Forebrain Axon Turning Point Is Maintained by Distinct Fgfr Isoforms but a Common Downstream Signal Transduction Mechanism.eNeuro. 2019 Apr 9;6(2):ENEURO.0086-19.2019. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0086-19.2019. eCollection 2019 Mar-Apr. eNeuro. 2019. PMID: 30993182 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of AKT inhibitor therapy in response and resistance to BRAF inhibition in melanoma.Mol Cancer. 2014 Apr 16;13:83. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-83. Mol Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24735930 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, Stephens P, Edkins S, et al. (2002) Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature 417 6892 949–54. - PubMed
-
- Slipicevic A, Holm R, Nguyen MT, Bohler PJ, Davidson B, et al. (2005) Expression of activated AKT and PTEN in malignant melanomas: relationship with clinical outcome. Am J Clin Pathol 124 4 528–36. - PubMed
-
- Karbowniczek M, Spittle CS, Morrison T, Wu H, Henske EP (2007) mTOR is activated in the majority of malignant melanomas. J Invest Dermatol 128 4 980–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

