Transcriptome analysis and SSR/SNP markers information of the blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala)
- PMID: 22880060
- PMCID: PMC3412804
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042637
Transcriptome analysis and SSR/SNP markers information of the blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala)
Abstract
Background: Blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala) is an herbivorous freshwater fish species native to China and has been recognized as a main aquaculture species in the Chinese freshwater polyculture system with high economic value. Right now, only limited EST resources were available for M. amblycephala. Recent advances in large-scale RNA sequencing provide a fast, cost-effective, and reliable approach to generate large expression datasets for functional genomic analysis, which is especially suitable for non-model species with un-sequenced genomes.
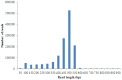
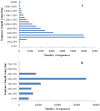
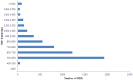
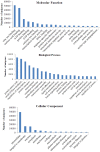
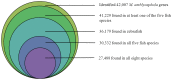
Methodology and principal findings: Using 454 pyrosequencing, a total of 1,409,706 high quality reads (total length 577 Mbp) were generated from the normalized cDNA of pooled M. amblycephala individuals. These sequences were assembled into 26,802 contigs and 73,675 singletons. After BLAST searches against the NCBI non-redundant (NR) and UniProt databases with an arbitrary expectation value of E(-10), over 40,000 unigenes were functionally annotated and classified using the FunCat functional annotation scheme. A comparative genomics approach revealed a substantial proportion of genes expressed in M. amblycephala tanscriptome to be shared across the genomes of zebrafish, medaka, tetraodon, fugu, stickleback, human, mouse, and chicken, and identified a substantial number of potentially novel M. amblycephala genes. A total number of 4,952 SSRs were found and 116 polymorphic loci have been characterized. A significant number of SNPs (25,697) and indels (23,287) were identified based on specific filter criteria in the M. amblycephala.
Conclusions: This study is the first comprehensive transcriptome analysis for a fish species belonging to the genus Megalobrama. These large EST resources are expected to be valuable for the development of molecular markers, construction of gene-based linkage map, and large-scale expression analysis of M. amblycephala, as well as comparative genome analysis for the genus Megalobrama fish species. The identified SSR and SNP markers will greatly benefit its breeding program and whole genome association studies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcriptome analysis and microsatellite discovery in the blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala) after challenge with Aeromonas hydrophila.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015 Jul;45(1):72-82. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2015.01.034. Epub 2015 Feb 12. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25681750
-
A global transcriptional analysis of Megalobrama amblycephala revealing the molecular determinants of diet-induced hepatic steatosis.Gene. 2015 Oct 10;570(2):255-63. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.06.025. Epub 2015 Jun 12. Gene. 2015. PMID: 26074088
-
Transcriptome Analysis of Blunt Snout Bream (Megalobrama amblycephala) Reveals Putative Differential Expression Genes Related to Growth and Hypoxia.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 10;10(11):e0142801. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142801. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26554582 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of sex-specific markers using genome re-sequencing in the blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala).BMC Genomics. 2024 Oct 15;25(1):963. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10884-0. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39407110 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome sequencing of mung bean (Vigna radiate L.) genes and the identification of EST-SSR markers.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 1;10(4):e0120273. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120273. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25830701 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome Analysis of the Innate Immunity-Related Complement System in Spleen Tissue of Ctenopharyngodon idella Infected with Aeromonas hydrophila.PLoS One. 2016 Jul 6;11(7):e0157413. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157413. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27383749 Free PMC article.
-
Genomics and transcriptomics of the Chinese mitten crabs (Eriocheir sinensis).Sci Data. 2023 Nov 30;10(1):843. doi: 10.1038/s41597-023-02761-4. Sci Data. 2023. PMID: 38036563 Free PMC article.
-
De novo assembly of the blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala) gill transcriptome to identify ammonia exposure associated microRNAs and their targets.Results Immunol. 2016 Mar 10;6:21-7. doi: 10.1016/j.rinim.2016.03.001. eCollection 2016. Results Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27504260 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Leucine Supplementation Improves Muscle Fiber Growth and Development by Activating AMPK/Sirt1 Pathway in Blunt Snout Bream (Megalobrama amblycephala).Aquac Nutr. 2022 Dec 21;2022:7285851. doi: 10.1155/2022/7285851. eCollection 2022. Aquac Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36860449 Free PMC article.
-
Benfotiamine, a Lipid-Soluble Analog of Vitamin B1, Improves the Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Function in Blunt Snout Bream (Megalobrama amblycephala) Fed High-Carbohydrate Diets by Promoting the AMPK/PGC-1β/NRF-1 Axis.Front Physiol. 2018 Sep 3;9:1079. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01079. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30233383 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li S, Cai W, Zhou B (1993) Variation in morphology and biochemical genetic markers among populations of blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala). Aquaculture 111: 117–127.
-
- Zhang D (2001) Study on genetic diversity of bluntnose black bream from Yunihu and Liangzi lakes. J China Three Gorges Univ 3: 282–284.
-
- Xu W, Xiong BX (2008) Advances in the research on genus Megalobrama in China. J Hydroecology 1 2 7–11.
-
- Ke H (1965) The artificial reproduction and culture experiment of Megalobrama amblycephala . Acta Hydrobiol Sin 5: 282–283.
-
- CAFS (Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences) (2001) Fishery Statistic Data. Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences, Beijing.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

