Increasing the multiplexing capacity of TMTs using reporter ion isotopologues with isobaric masses
- PMID: 22880955
- PMCID: PMC3715028
- DOI: 10.1021/ac301572t
Increasing the multiplexing capacity of TMTs using reporter ion isotopologues with isobaric masses
Abstract
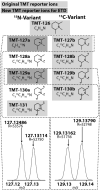
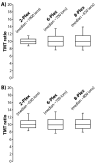
Quantitative mass spectrometry methods offer near-comprehensive proteome coverage; however, these methods still suffer with regards to sample throughput. Multiplex quantitation via isobaric chemical tags (e.g., TMT and iTRAQ) provides an avenue for mass spectrometry-based proteome quantitation experiments to move away from simple binary comparisons and toward greater parallelization. Herein, we demonstrate a straightforward method for immediately expanding the throughput of the TMT isobaric reagents from 6-plex to 8-plex. This method is based upon our ability to resolve the isotopic shift that results from substituting a (15)N for a (13)C. In an accommodation to the preferred fragmentation pathways of ETD, the TMT-127 and -129 reagents were recently modified such that a (13)C was exchanged for a (15)N. As a result of this substitution, the new TMT reporter ions are 6.32 mDa lighter. Even though the mass difference between these reporter ion isotopologues is incredibly small, modern high-resolution and mass accuracy analyzers can resolve these ions. On the basis of our ability to resolve and accurately measure the relative intensity of these isobaric reporter ions, we demonstrate that we are able to quantify across eight samples simultaneously by combining the (13)C- and (15)N-containing reporter ions. Considering the structure of the TMT reporter ion, we believe this work serves as a blueprint for expanding the multiplexing capacity of the TMT reagents to at least 10-plex and possibly up to 18-plex.
Figures




References
-
- Huttlin EL, Jedrychowski MP, Elias JE, Goswami T, Rad R, Beausoleil SA, Villen J, Haas W, Sowa ME, Gygi SP. A Tissue-Specific Atlas of Mouse Protein Phosphorylation and Expression. Cell. 2010;143(7):1174–1189. - PMC - PubMed
- Nagaraj N, Wisniewski JR, Geiger T, Cox J, Kircher M, Kelso J, Paabo S, Mann M. Deep proteome and transcriptome mapping of a human cancer cell line. Mol Syst Biol. 2011;7 - PMC - PubMed
- Beck M, Schmidt A, Malmstroem J, Claassen M, Ori A, Szymborska A, Herzog F, Rinner O, Ellenberg J, Aebersold R. The quantitative proteome of a human cell line. Mol Syst Biol. 2011;7 - PMC - PubMed
- Phanstiel DH, Brumbaugh J, Wenger CD, Tian SL, Probasco MD, Bailey DJ, Swaney DL, Tervo MA, Bolin JM, Ruotti V, Stewart R, Thomson JA, Coon JJ. Proteomic and phosphoproteomic comparison of human ES and iPS cells. Nature Methods. 2011;8(10):821–U84. - PMC - PubMed
- de Godoy LMF, Olsen JV, Cox J, Nielsen ML, Hubner NC, Frohlich F, Walther TC, Mann M. Comprehensive mass-spectrometry-based proteome quantification of haploid versus diploid yeast. Nature. 2008;455(7217):1251–U60. - PubMed
-
- DeSouza LV, Taylor AM, Li W, Minkoff MS, Romaschin AD, Colgan TJ, Siu KWM. Multiple reaction monitoring of mTRAQ-labeled peptides enables absolute quantification of endogenous levels of a potential cancer marker in cancerous and normal endometrial tissues. Journal of Proteome Research. 2008;7(8):3525–3534. - PubMed
- Gygi SP, Rist B, Gerber SA, Turecek F, Gelb MH, Aebersold R. Quantitative analysis of complex protein mixtures using isotope-coded affinity tags. Nature Biotechnology. 1999;17(10):994–999. - PubMed
- Li JX, Steen H, Gygi SP. Protein profiling with cleavable isotope-coded affinity tag (cICAT) reagents – The yeast salinity stress response. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics. 2003;2(11):1198–1204. - PubMed
- Hansen KC, Schmitt-Ulms G, Chalkley RJ, Hirsch J, Baldwin MA, Burlingame AL. Mass spectrometric analysis of protein mixtures at low levels using cleavable C-13-isotope-coded affinity tag and multidimensional chromatography. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics. 2003;2(5):299–314. - PubMed
- Ong SE, Blagoev B, Kratchmarova I, Kristensen DB, Steen H, Pandey A, Mann M. Stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture, SILAC, as a simple and accurate approach to expression proteomics. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics. 2002;1(5):376–386. - PubMed
- Hsu JL, Huang SY, Chow NH, Chen SH. Stable-isotope dimethyl labeling for quantitative proteomics. Analytical Chemistry. 2003;75(24):6843–6852. - PubMed
-
- Hsu JL, Huang SY, Chen SH. Dimethyl multiplexed labeling combined with microcolumn separation and MS analysis for time course study in proteomics. Electrophoresis. 2006;27(18):3652–3660. - PubMed
- Morano C, Zhang X, Fricker LD. Multiple Isotopic Labels for Quantitative Mass Spectrometry. Analytical Chemistry. 2008;80(23):9298–9309. - PMC - PubMed
- Boersema PJ, Aye TT, van Veen TAB, Heck AJR, Mohammed S. Triplex protein quantification based on stable isotope labeling by peptide dimethylation applied to cell and tissue lysates. Proteomics. 2008;8(22):4624–4632. - PubMed
-
- Thompson A, Schafer J, Kuhn K, Kienle S, Schwarz J, Schmidt G, Neumann T, Hamon C. Tandem mass tags: A novel quantification strategy for comparative analysis of complex protein mixtures by MS/MS. Analytical Chemistry. 2003;75(8):1895–1904. - PubMed
- Dayon L, Hainard A, Licker V, Turck N, Kuhn K, Hochstrasser DF, Burkhard PR, Sanchez JC. Relative quantification of proteins in human cerebrospinal fluids by MS/MS using 6-plex isobaric tags. Analytical Chemistry. 2008;80(8):2921–2931. - PubMed
- Ross PL, Huang YLN, Marchese JN, Williamson B, Parker K, Hattan S, Khainovski N, Pillai S, Dey S, Daniels S, Purkayastha S, Juhasz P, Martin S, Bartlet-Jones M, He F, Jacobson A, Pappin DJ. Multiplexed protein quantitation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using amine-reactive isobaric tagging reagents. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics. 2004;3(12):1154–1169. - PubMed
- Choe L, D’Ascenzo M, Relkin NR, Pappin D, Ross P, Williamson B, Guertin S, Pribil P, Lee KH. 8-Plex quantitation of changes in cerebrospinal fluid protein expression in subjects undergoing intravenous immunoglobulin treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. Proteomics. 2007;7(20):3651–3660. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

