Endosomal proteolysis regulates calcitonin gene-related peptide responses in mesenteric arteries
- PMID: 22881710
- PMCID: PMC3525870
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02129.x
Endosomal proteolysis regulates calcitonin gene-related peptide responses in mesenteric arteries
Abstract
Background and purpose: Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) is a potent vasodilator, implicated in the pathogenesis of migraine. CGRP activates a receptor complex comprising, calcitonin receptor-like receptor (CLR) and receptor activity-modifying protein 1 (RAMP1). In vitro studies indicate recycling of CLR●RAMP1 is regulated by degradation of CGRP in early endosomes by endothelin-converting enzyme-1 (ECE-1). However, it is not known if ECE-1 regulates the resensitization of CGRP-induced responses in functional arterial tissue.
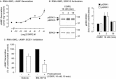
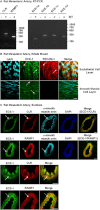
Experimental approach: CLR, ECE-1a-d and RAMP1 expression in rat mesenteric artery smooth muscle cells (RMA-SMCs) and mesenteric arteries was analysed by RT-PCR and by immunofluorescence and confocal microscopy. CGRP-induced signalling in cells was examined by measuring cAMP production and ERK activation. CGRP-induced relaxation of arteries was measured by isometric wire myography. ECE-1 was inhibited using the specific inhibitor, SM-19712.
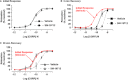
Key results: RMA-SMCs and arteries contained mRNA for CLR, ECE-1a-d and RAMP1. ECE-1 was present in early endosomes of RMA-SMCs and in the smooth muscle layer of arteries. CGRP induced endothelium-independent relaxation of arteries. ECE-1 inhibition had no effect on initial CGRP-induced responses but reduced cAMP generation in RMA-SMCs and vasodilation in mesenteric arteries responses to subsequent CGRP challenges.
Conclusions and implications: ECE-1 regulated the resensitization of responses to CGRP in RMA-SMCs and mesenteric arteries. CGRP-induced relaxation did not involve endothelium-derived pathways. This is the first report of ECE-1 regulating CGRP responses in SMCs and arteries. ECE-1 inhibitors may attenuate an important vasodilatory pathway, implicated in primary headaches and may represent a new therapeutic approach for the treatment of migraine.
© 2012 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2012 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Endothelin-converting enzyme-1 regulates endosomal sorting of calcitonin receptor-like receptor and beta-arrestins.J Cell Biol. 2007 Dec 3;179(5):981-97. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200704053. Epub 2007 Nov 26. J Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 18039931 Free PMC article.
-
Binding and functional pharmacological characteristics of gepant-type antagonists in rat brain and mesenteric arteries.Vascul Pharmacol. 2017 Mar;90:36-43. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2017.02.001. Epub 2017 Feb 10. Vascul Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28192258
-
Long-lasting physiological antagonism of calcitonin gene-related peptide towards endothelin-1 in rat mesenteric arteries and human coronary arteries.Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Nov 15;720(1-3):303-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.10.012. Epub 2013 Oct 18. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24140435
-
[Regulatory mechanisms of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) in skin inflammation].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2012;132(11):1211-5. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.12-00232-1. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2012. PMID: 23123709 Review. Japanese.
-
The Role of Calcitonin Gene Related Peptide (CGRP) in Neurogenic Vasodilation and Its Cardioprotective Effects.Front Physiol. 2018 Sep 19;9:1249. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01249. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30283343 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Update on the pharmacology of calcitonin/CGRP family of peptides: IUPHAR Review 25.Br J Pharmacol. 2018 Jan;175(1):3-17. doi: 10.1111/bph.14075. Epub 2017 Nov 28. Br J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29059473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CGRP physiology, pharmacology, and therapeutic targets: migraine and beyond.Physiol Rev. 2023 Apr 1;103(2):1565-1644. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00059.2021. Epub 2022 Dec 1. Physiol Rev. 2023. PMID: 36454715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of proteolysis in regulation of GPCR function.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Feb;168(3):576-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02234.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23043558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vampire Venom: Vasodilatory Mechanisms of Vampire Bat (Desmodus rotundus) Blood Feeding.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Jan 8;11(1):26. doi: 10.3390/toxins11010026. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30626071 Free PMC article.
-
Pipeline for development of acylated peptide based CGRP receptor antagonist with extended half-life for migraine treatment.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 13;15(1):1870. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84547-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39805895 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahn K, Sisneros AM, Herman SB, Pan SM, Hupe D, Lee C, et al. Novel selective quinazoline inhibitors of endothelin converting enzyme-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;243:184–190. - PubMed
-
- Barnes K, Turner AJ. Endothelin converting enzyme is located on alpha-actin filaments in smooth muscle cells. Cardiovasc Res. 1999;42:814–822. - PubMed
-
- Bellamy JL, Cady RK, Durham PL. Salivary levels of CGRP and VIP in rhinosinusitis and migraine patients. Headache. 2006;46:24–33. - PubMed
-
- Brain SD, Grant AD. Vascular actions of calcitonin gene-related peptide and adrenomedullin. Physiol Rev. 2004;84:903–934. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

