Chapter 5: Actual and counterfactual smoking prevalence rates in the U.S. population via microsimulation
- PMID: 22882892
- PMCID: PMC3478148
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1539-6924.2011.01775.x
Chapter 5: Actual and counterfactual smoking prevalence rates in the U.S. population via microsimulation
Abstract
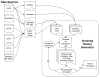
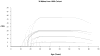
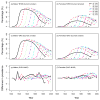
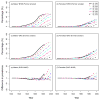
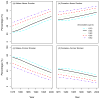
The smoking history generator (SHG) developed by the National Cancer Institute simulates individual life/smoking histories that serve as inputs for the Cancer Intervention and Surveillance Modeling Network (CISNET) lung cancer models. In this chapter, we review the SHG inputs, describe its outputs, and outline the methodology behind it. As an example, we use the SHG to simulate individual life histories for individuals born between 1890 and 1984 for each of the CISNET smoking scenarios and use those simulated histories to compute the corresponding smoking prevalence over the period 1975-2000.
© 2012 Society for Risk Analysis.
Figures

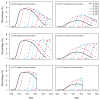

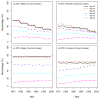
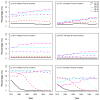

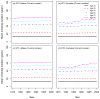

References
-
- Moolgavkar SH, Knudson AG., Jr Mutation and cancer: a model for human carcinogenesis. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 1981;66(6):1037–1052. - PubMed
-
- Hazelton WD, Clements MS, Moolgavkar SH. Multistage carcinogenesis and lung cancer mortality in three cohorts. Cancer epidemiology, biomarkers & prevention. 2005;14(5):1171–1181. - PubMed
-
- Meza R, Hazelton WD, Colditz GA, Moolgavkar SH. Analysis of lung cancer incidence in the Nurses’ Health and the Health Professionals’ Follow-Up Studies using a multistage carcino-genesis model. Cancer causes & control. 2008;19(3):317–328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

