Fibroblast growth factor 23, high-sensitivity cardiac troponin, and left ventricular hypertrophy in CKD
- PMID: 22883134
- PMCID: PMC3525738
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2012.06.022
Fibroblast growth factor 23, high-sensitivity cardiac troponin, and left ventricular hypertrophy in CKD
Abstract
Background: Detectable levels of cardiac troponins are common in individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD), even in the absence of symptomatic cardiovascular disease. Abnormal cardiac troponin values are associated with coronary artery disease and left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) and predict poor clinical outcomes. Elevated levels of fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF-23) contribute to LVH in CKD. We investigated the association of FGF-23 and hs-cTnI (high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I) and hs-cTnT (high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T) levels in CKD and examined the role of LVH in this association.
Study design: Cross-sectional observational study.
Setting & participants: 153 stable outpatients with non-dialysis-dependent CKD.
Predictor: The primary predictor was FGF-23 level.
Outcomes: hs-cTnI, hs-cTnT.
Measurements: FGF-23, hs-cTnI, hs-cTnT; left ventricular mass index (LVMI) assessed by echocardiography; coronary artery calcification (CAC) measured by computed tomography. LVMI and CAC were evaluated as potential mediators of the effect of FGF-23 on hs-cTnI/T.
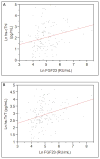
Results: Mean age was 64 ± 12 (SD) years, mean estimated glomerular filtration rate was 34 ± 11 mL/min/1.73 m(2), median FGF-23 level was 120 (25th-75th percentile, 79-223) reference unit (RU)/mL, median hs-cTnI level was 6.5 (25th-75th percentile, 3.5-14.5) pg/mL, and median hs-cTnT level was 16.8 (25th-75th percentile, 11.1-33.9) pg/mL. cTnI and cTnT concentrations were higher than the 99th percentile of a healthy population in 42% and 61% of patients, respectively. In unadjusted and multivariable-adjusted analyses, hs-cTnI/T levels were associated significantly with FGF-23 levels. Adjusting for LVMI, but not CAC, weakened the association of FGF-23 and hs-cTnI/T levels.
Limitations: Vitamin D levels were not measured. The prevalence of coronary artery disease may have been underestimated because it was ascertained by self-report.
Conclusions: Minimally elevated cTnI and cTnT levels, detectable by high-sensitivity assays, are associated with elevated FGF-23 levels in stable outpatients with CKD. FGF-23-associated LVH may contribute to detectable hs-cTnI/T levels observed in non-dialysis-dependent patients with CKD.
Copyright © 2012 National Kidney Foundation, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(13):1296–1305. - PubMed
-
- US Renal Data System. USRDS 2011 Annual Data Report: Atlas of Chronic Kidney Disease and End-Stage Renal Disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis. 2012;59(1 suppl 1):e1–e420. - PubMed
-
- Middleton RJ, Parfrey PS, Foley RN. Left ventricular hypertrophy in the renal patient. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001;12(5):1079–1084. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

